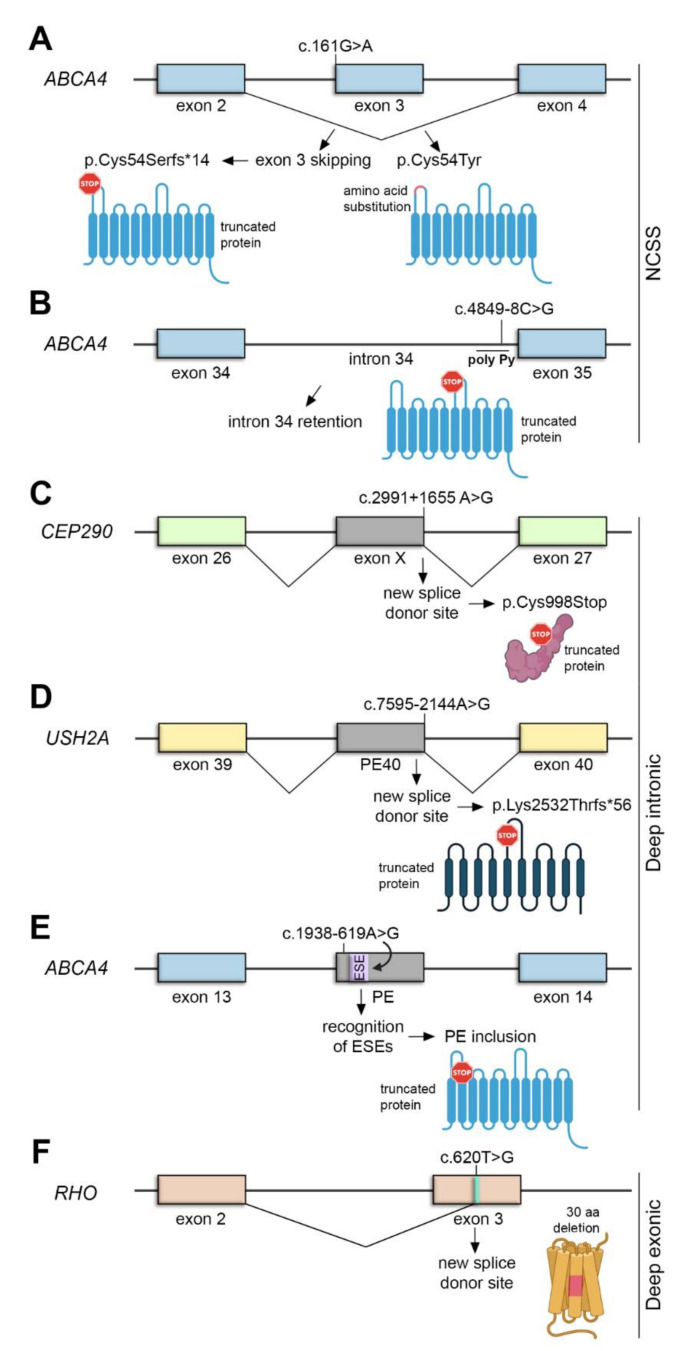
Figure 4.
Overview of cis acting mutations altering splicing: NCSS (A,B), deep intronic (C–E) and deep exonic variants (F). (A) ABCA4 exon 3 shows a weak natural exon skipping. The c.161G>A mutation increase exon 3 skipping (producing a truncated ABCA4 protein) and the p.Cys54Tyr amino acid substitution. (B) The ABCA4 c.4849-8C>G mutation lowers the value of the poly-Py tract, thus causing intron 34 retention and production of a truncated protein. (C) The CEP290 c.2991+1655A>G mutation creates a new SDS, that induce inclusion of a cryptic exon (exon X) encoding a premature stop codon. (D) The USH2A c.7595-2144A>G mutation creates a new SDS that causes pseudoexon inclusion (PE40) and introduces a premature stop codon. (E) The ABCA4 c.1938-619A>G mutation, located in a cryptic pseudoexon (PE), leads to the recognition of ESEs that promote PE inclusion, leading to the truncation of the protein. (F) The RHO c.620T>G mutation creates a strong splice donor site that results in a 30 amino acid in-frame deletion.