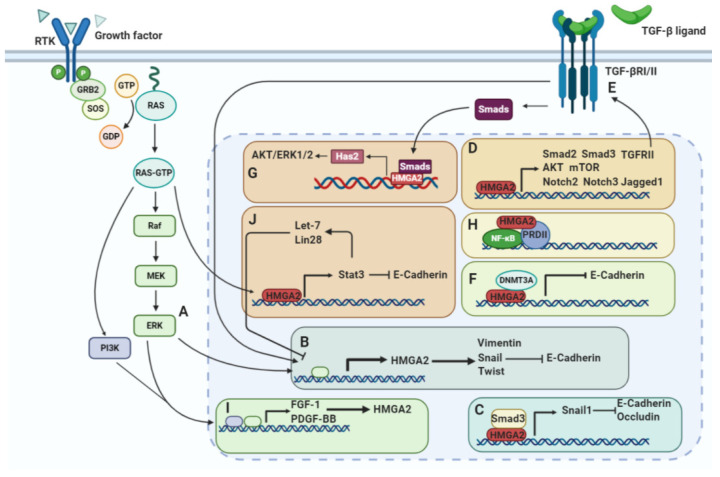
Figure 5.
HMGA2 induces EMT by activation of different signaling transducers. (A) HMGA2 expression is induced by the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. (B) HMGA2 promotes the expression of vimentin, Snail and Twist and reduces E-cadherin expression. (C) Colocalization of HMGA2 and smad3 on the Snail1 promotor induces expression of Snail1, and then Snail1 inhibits E-cadherin and occludin expression. (D) HMGA2 controls activation of the TGFβ, MAPK, and Notch pathways by regulating the main elements, including Smad2, Smad3, TGFβRII, AKT, mTOR, Notch2, Notch3, and Jagged1. (E) TGFβRII induced by HMGA2 increases activity of the TGFβ signaling pathway, which promotes HMGA2 expression in a positive feedback loop. (F) Long-term TGFβ signaling activation causes HMGA2 to recruit DNMT3A to the E-cadherin gene promoter and inactivates its transcription by DNA methylation. (G) During TGFβ pathway signaling, Smads cooperate with HMGA2 to bind to the Has2 promoter, inducing expression of Has2, which then activates AKT/ERK1/2 signaling. (H) HMGA2 enhances the binding of NFκB to the positive regulatory domain II (PRDII) transcription factor. (I) Regulators downstream of the MAPK and PI3K pathways, including FGF-1 and platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB), induce HMGA2 expression. (J) HMGA2 induces the expression of STAT3. Then, STAT3 activation promotes EMT by reducing E-cadherin expression. STAT3 also activates the miRNAs let-7 and lin-28, which suppress HMGA2 expression.