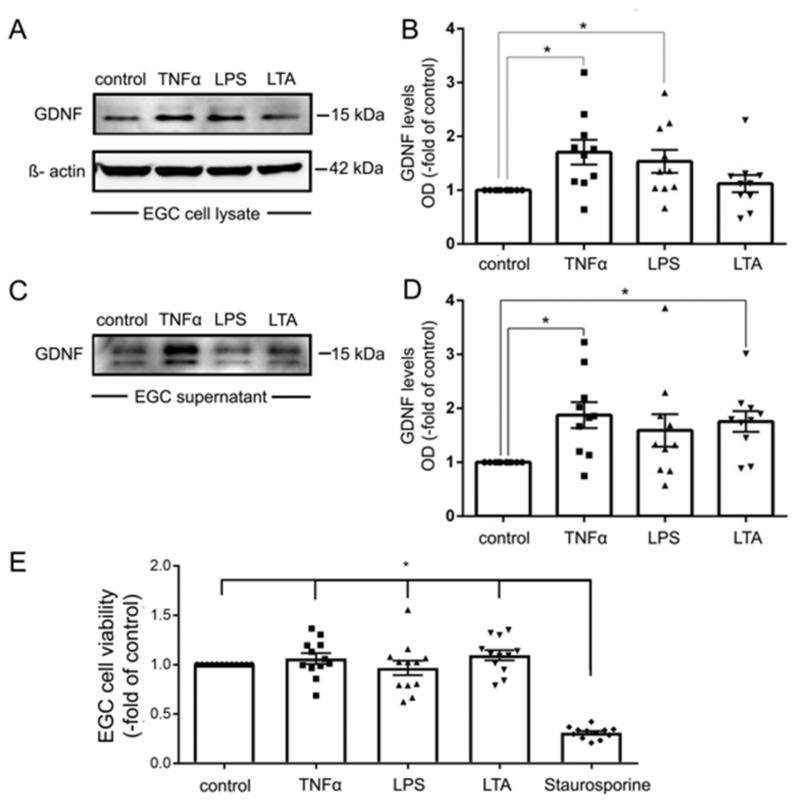
Figure 7.
Tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) increased the expression and secretion of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) in enteric glial cells (EGC). (A). Representative Western blot of EGC cell lysates showing that TNFα and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) but not lipoteichoic acid (LTA) led to increased expression of GDNF, membranes were reprobed for β-actin to ensure equal protein loading; (n = 9). (B). Quantification of all Western blots showed a significantly increased expression of GDNF by TNFα and LPS but not by LTA; (n = 9; * = p < 0.05, Kruskal Wallis Test); Control = Caco2 monolayer without treatment. (C). Representative Western blot of EGC cell culture supernatants is shown which demonstrates increased release of GDNF by TNFα and LTA but not LPS; (n = 9). (D). Quantification of all Western blots showed a significantly increased release of GDNF by TNFα and LTA but not by LPS (n = 9; * = p < 0.05, Kruskal Wallis Test); Control = Caco2 supernatant without treatment. (E). MTT assays served to test for cell viability. Except for incubation with staurosporine EGC cell viability was not changed for the different experimental conditions (n = 10; * = p < 0.05 control, TNFα, LPS, LTA vs. Strauosporine; Kruskal Wallis Test); Control = Caco2 monolayer without treatment.