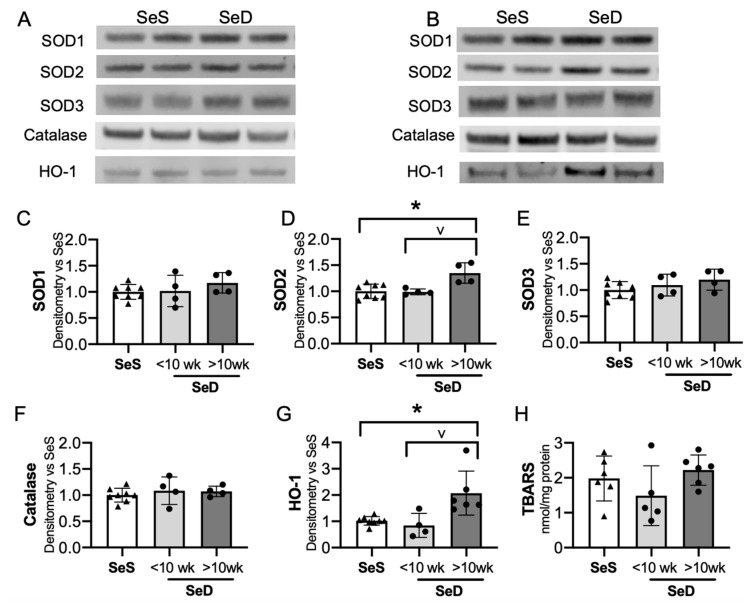
Figure 6.
Neonates born to dams with prolonged Se deficient exhibit increased hepatic SOD2 and HO-1. C57Bl/6 mice were placed on diets that differed only in Se content, either 0.4 ppm or <0.01 ppm of sodium selenite. Breeding was initiated after 2–4 weeks on diet and natural delivery was allowed. Hepatic organ homogenate was evaluated on day of birth. Each data point represents either a female or male from each litter; each individual point is an average of two mice. (A) Representative Western blots of hepatic SOD1, SOD2, SOD3, catalase, and HO-1 for SeS samples and SeD samples born to dams who received <10 weeks SeD diet, (B) representative Western blots of hepatic SOD1, SOD2, SOD3, catalase, and HO-1 for SeS samples and SeD samples born to dams who received >10 weeks SeD diet, densitometric analysis of (C) SOD1, (D) SOD2, (E) SOD3, and (F) Catalase, (G) HO-1 protein content expression. Results are normalized to total protein stain and expressed as a ratio to SeS mice. (H) TBARS expression, expressed as a ratio to SeS mice N = 4–8 for all groups. Data are presented as mean (±SEM), * p < 0.05 vs. SeS control, by multiple comparison after one-way ANOVA, ∨ p < 0.05 vs. SeD <10 weeks by multiple comparisons after one-way ANOVA.