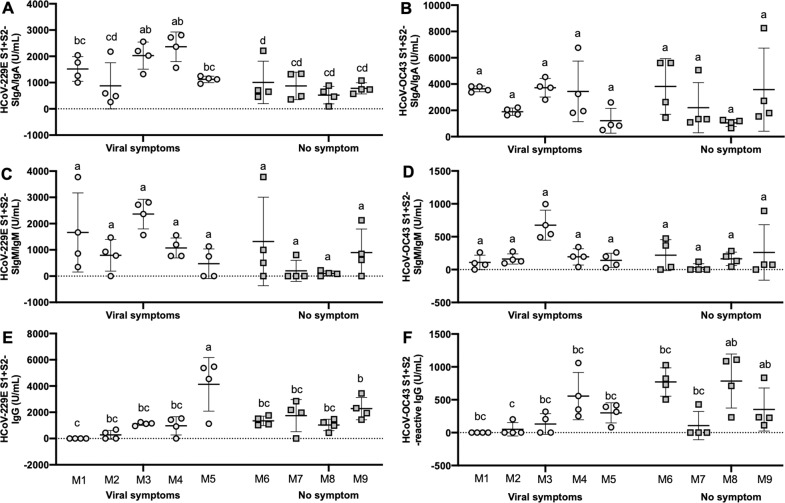
Fig. 4. Influence of viral symptoms on the levels of antibodies reactive to common human coronaviruses (HCoVs) in human milk.
A HCoV-229E S1 + S2-reactive SIgA/IgA, B HCoV-OC43 S1 + S2-reactive SIgA/IgA, C HCoV-229E S1 + S2-reactive SIgM/IgM, D HCoV-OC43 S1 + S2-reactive SIgM/IgM, E HCoV-229E S1 + S2-reactive IgG, and F HCoV-OC43 S1 + S2-reactive IgG. Letters a–c show statistically significant differences between groups (p < 0.05) using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. Values are means ± SD, where n = 5 for mothers in the viral symptom group and n = 4 for mothers in the no-symptom group. Human milk samples were collected at four different time points across postpartum time for each mother.