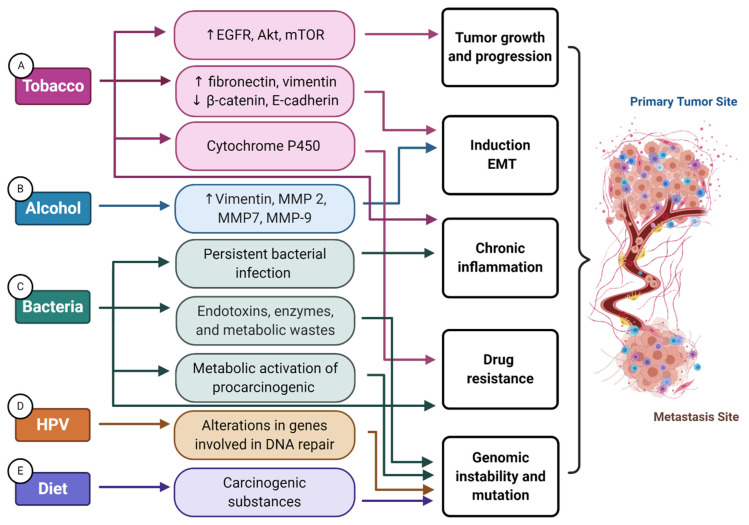
Figure 2.
Mechanisms involved in environmental factor support of the onset and progression of head and neck cancer. (A) The expression of alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) promotes proliferation and migration through the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), protein kinase B (Akt), mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors. Nicotine upregulates the expression of mesenchymal proteins (fibronectin and vimentin), whereas it downregulates epithelial proteins (beta-catenin and E-cadherin), thereby supporting cell motility and invasion through induction of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). Nicotine can perturb drug efficacy via cytochrome P450 (CYP)-mediated metabolism, glucuronidation, and/or protein binding, which may impact the efficacy of anticancer drugs. Tobacco consumption also promotes a pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment, further supporting tumor growth. (B) Alcohol is capable of directly upregulating vimentin, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-7, and MMP-9, promoting an EMT invasive phenotype and extracellular matrix remodeling. (C) Particular bacteria participate in the metabolic activation of carcinogenic chemicals, like acetaldehyde, that can promote tumorigenesis through genomic mutations. Chronic inflammation prompted by persistent bacterial infection also supports multiple hallmark capabilities. Bacteria products like endotoxins, enzymes, and metabolic wastes might cause DNA damage, consequently altering cell cycle control and signaling pathways that can lead to even further genomic instability and mutation. Certain immune cell responses to gut commensal bacteria are also associated with immunotherapy response. (D) HPV-related tumors carry more frequent alterations in genes involved in DNA repair, such as PRKDC, potentially hindering a cell’s capacity for DNA repair. (E) Lastly, red meat and processed meats also contain carcinogenic substances that can cause genomic instability and mutations.