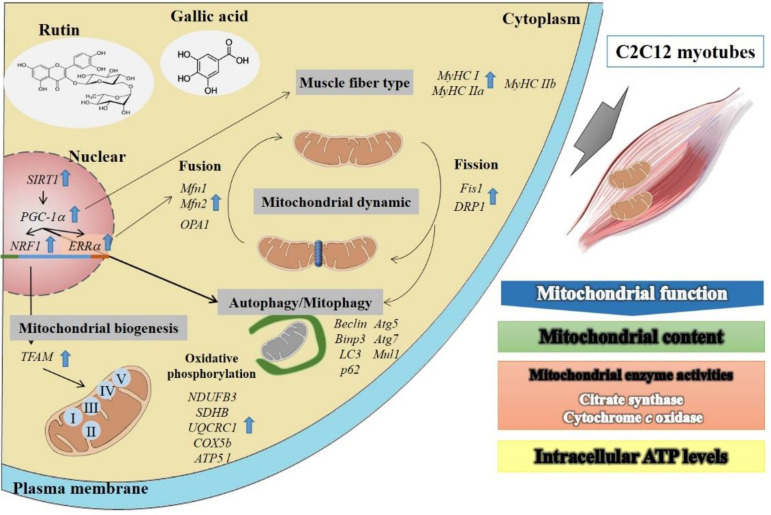
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of action mechanism by gallic acid and rutin on mitochondrial functions in C2C12 myotubes. Improvement of functions of the mitochondrial network will result in increased exercise performance. The mitochondria in skeletal muscle are dynamically balanced. By enhancing the performance of genes, such as mitochondrial synthesis, fusion/fission, and mitochondrial autophagy, it can enhance mitochondrial function and improve metabolic dysfunction diseases. Gallic acid and rutin are the most potent activators of mitochondrial function, which is mediated through SIRT1 pathway. The results show that it has the best performance in enhancing the mitochondrial function of C2C12 myotube cells (mitochondrial DNA content, mitochondrial number, enzyme activities, and ATP content). It can further promote the downstream molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial biosynthesis genes (PGC-1α, NRF1, ERRα, and TFAM), mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (NDUFB3, SDHB, UQCRC1, COX5b, and ATP5 l), oxidized muscle fibers (MyHC I and MyHC IIa), fusion/fission (Mfn1, Mfn2, OPA1, DRP1, and Fis1), and mitochondrial autophagy (Atg5, Atg7, Beclin, Bnip3, LC3II, Mul1, and p62) gene expressions to improve skeletal muscle endurance. Therefore, gallic acid and rutin may be beneficial against exercise performance and anti-fatigue action.