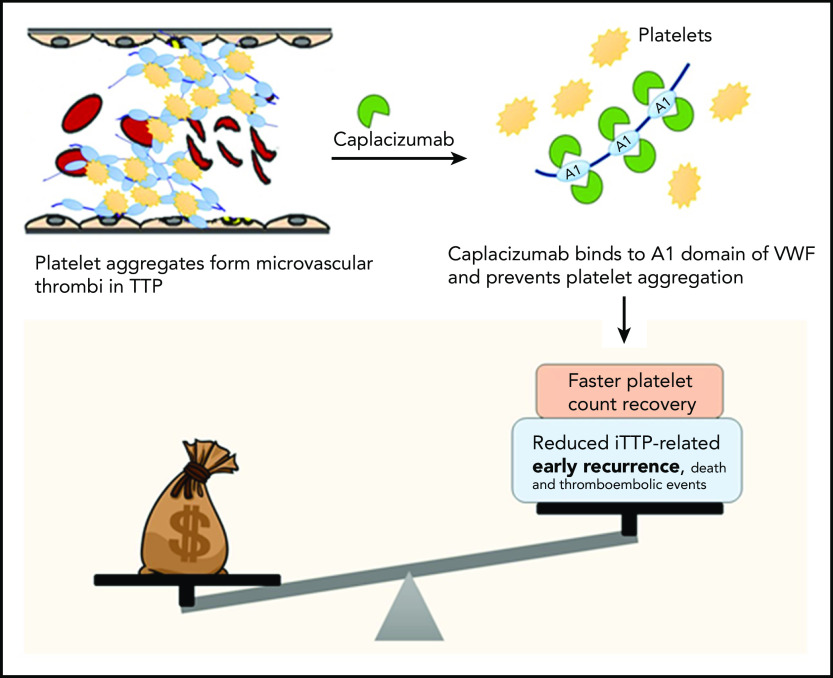
Costs vs benefits of caplacizumab for TTP. In TTP, platelets form aggregates by binding to ultra-large multimers of VWF; these aggregate form microthrombi that lead to ischemic organ damage. Caplacizumab is a nanobody directed against domain A1 of VWF, which prevents VWF-platelet interactions, leading to faster resolution of thrombocytopenia in TTP. In clinical trials, adding caplacizumab to standard-of-care therapy led to faster time to platelet count recovery (and reduced duration of plasma exchange and hospitalization, as well as a reduction in the composite endpoint of iTTP-related death, recurrence, and major thromboembolic events, which was driven primarily by the reduction in early recurrences). However, the current analysis demonstrates that caplacizumab is not cost effective at its current list price in the United States.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.