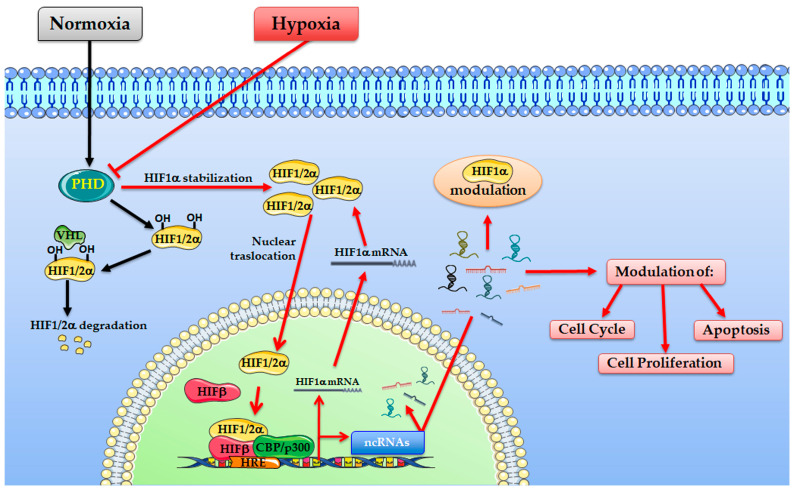
Figure 1.
Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) complex transcriptionally activates non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in response to hypoxia. Under normoxia (black arrows), HIF-1/2α subunits are subjected to hydroxylation by prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes (PHDs) and other prolyl hydroxylases. Hydroxylated HIF-1/2α subunits are recognized by VHL proteins and targeted for subsequent ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Under hypoxia (red arrows), low pO2 results in HIF-1/2α accumulation, nuclear translocation and dimerization with HIF-b, finally, after recruitment of CBP/p300, the transcription initiation complex binds the promoter of target genes inducing their expression. Among the hypoxia-induced RNAs, the ncRNAs (miRNAs or lncRNAs) will be involved in different pathways, regulating cell proliferation, cell cycle and cell death. Moreover, some of these can regulate HIF itself.