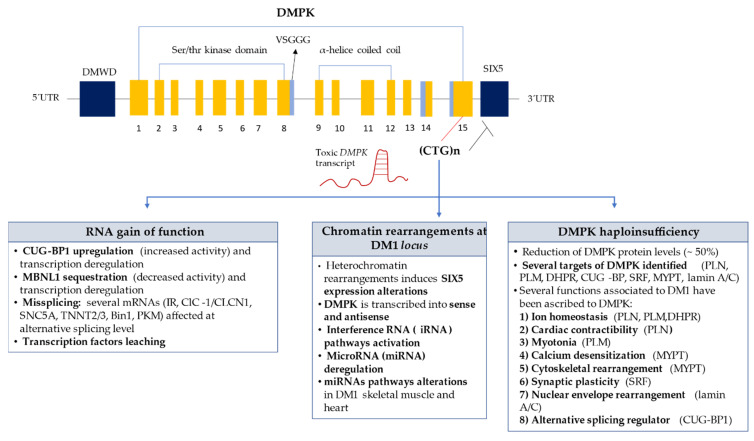
Figure 1.
Molecular Mechanisms in DM1. Toxic CUG-containing transcripts forms secondary structures and accumulates in the nucleus of DM1 cells, causing multisystemic effects of DM1 throughout RNA gain-of-function mechanism, Chromatin rearrangements at the DM1 locus and DMPK haploinsufficiency [6,21,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. CUGBP1-CUGBP-Elav-like family member 1; MBLN1—muscleblind-like protein 1; Insulin receptor (IR); DHPR—Voltage-Dependent L-type Calcium; PLM—Phospholemman, PLN—Phospholamban; SRF—Serum response factor; MYPT—Myosin phosphatase; CIC/CLCN1—Voltage-gated chloride channel; SNC5A—Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha; TNNT2/3—Troponin T 2/3; Bin1—Bridging integrator 1; PKM—Pyruvate kinase.