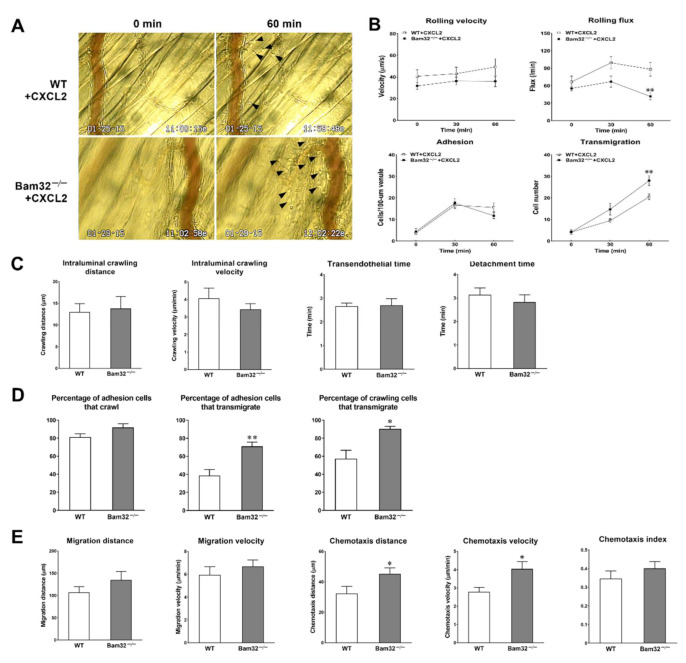
Figure 1.
Effect of Bam32 deficiency on CXCL2-induced neutrophil recruitment in the mouse cremaster muscle. (A) Representative micrographs from intravital video microscopy showing a postcapillary venule and the surrounding tissue of the cremaster muscle with transmigrated neutrophils (arrow head) before (0 min) and at 60 min following the placement of CXCL2-containing gel (out of the view, 350-µm distant from the venule) in wild-type (WT) and Bam32−/− mice (magnification: 100×). (B) Intravascular leukocyte rolling velocity, rolling flux, and numbers of adherent neutrophils (cells/100-µm venule) and emigrated neutrophils (cells/235 × 208 µm2 field) before (0 min) and 30 and 60 min after the placement of CXCL2-containing gel on the cremaster muscle of WT and Bam32−/− mice. (C) The crawling distance (µm), crawling velocity (µm/min), transendothelial time (min), and detachment time (min) during 60-min video recording following the placement of CXCL2-containing gel in WT and Bam32−/− mice. (D) The percentage of adherent cells that crawled on the luminal surface of the endothelium, the percentage of adhesion cells that transmigrated across the endothelium, and the percentage of crawling cells that transmigrated across the endothelium during 60-min video recording following the placement of CXCL2-containing gel in WT and Bam32−/− mice. (E) The migration distance (µm), chemotaxis distance (µm), migration velocity (µm/min), chemotaxis velocity (µm/min), and chemotaxis index of neutrophil chemotaxis in extravascular tissue during 60 min following the placement of CXCL2-containing gel on the cremaster muscle of WT and Bam32−/− mice (averaged from >80 cells). (B−E): mean ± SEM of 8 mice per group. * and ** indicate significant differences (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively) from WT mice.