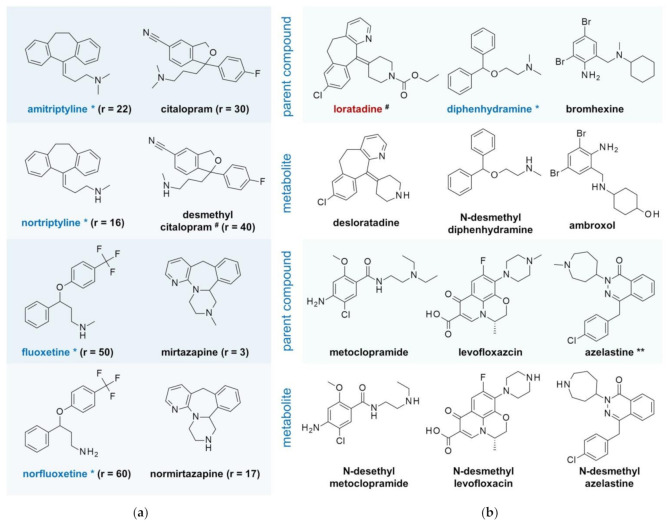
Figure 2.
Lysosomotropic candidates and pulmonary tissue accumulation: (a) pairs of confirmed (blue colored) and potential lysosomotropic drugs and their N-desmethyl metabolites with proved enrichment in pulmonary tissue (ratio of pulmonary tissue/plasma concentration r > 1) [40,41,42]. (#) Ratio determined in rats, (*) lysosomotropism is confirmed [26]; (b) candidates for (systemic) prophylaxis of viral infection and transition to COVID-19. The over-the-counter drugs bromhexine, ambroxol, loratadine, desloratadine, azelastine, and diphenhydramine are assumed to contribute significantly to viral infection prophylaxis and frequency in less affected countries such as Germany. Unless indicated, lysosomotropism is highly probable, but not confirmed. (*) lysosomotropism is confirmed, (#) no lysosomotropism, (**) nasal and ophthalmic H1-antihistamine. Levofloxacin exhibits anti-inflammatory effects on prominent inflammatory messengers in mice with LPS-induced acute lung injuries [43], comparable to NB 06 in LPS-induced inflammation [22].