Figure 6. DNA damage accumulation concurred with perinuclear glycine-alanine (GA) dipeptide repeat protein foci in C9ORF72 spinal MNs over ageing.
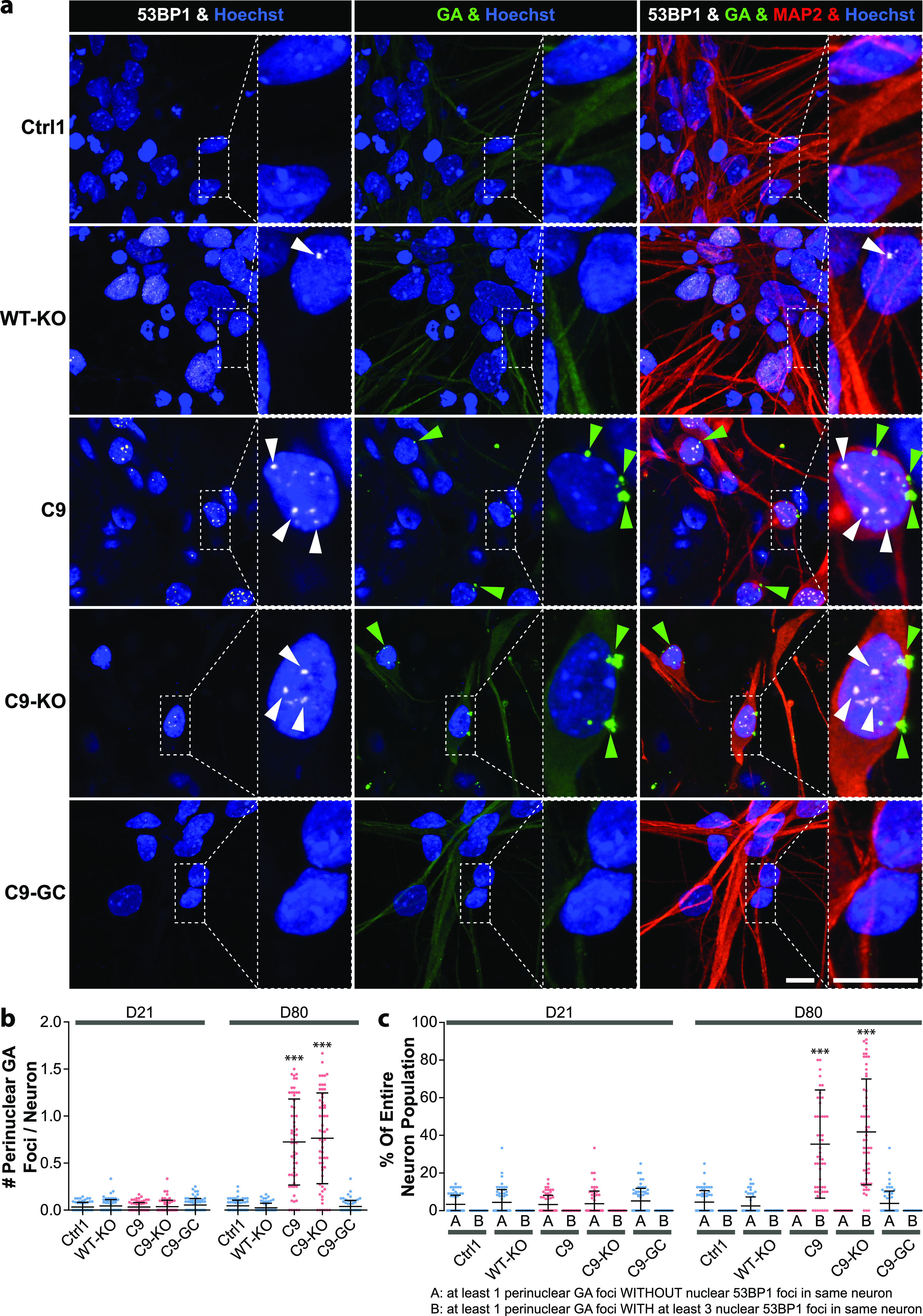
(A) DNA double-strand break (DSB) marker 53BP1 (in white) in Hoechst-positive nuclei (in blue) and perinuclear GA foci (in green) in MAP2-positive neurons (in red) were revealed by confocal IF microscopy at D80 endpoints (Fig 3). Dotted boxed areas in image galleries are shown magnified on the right. Note the striking nuclear accumulation of 53BP1-positive nuclear foci (white arrowheads) in parental C9 and C9-KO that was phenocopied by WT-KO. Furthermore, perinuclear GA foci (green arrowheads) concurred with nuclear 53BP1 accumulation within the same neuron in C9 and C9-KO. Conversely, DSBs and GA foci were nearly absent in C9-GC and parental Ctrl1. Arrowheads point only to arbitrary examples. Scale bars = 10 μm. (B) Quantification of (A), number of perinuclear GA foci in MAP2-positive neurons at D21 versus D80, displayed as scatterplots of foci counts per neuron and image with mean (center line) and SD range (whiskers) indicated in black. For images at D21 refer to Fig S5. Note nearly absent GA foci at D21 in all lines versus drastic GA accumulation at D80 in parental C9 and C9-KO. (C) Quantification of (A), percentage of MAP2-positive neurons with at least one perinuclear GA focus without (A) nuclear DSBs within the same cell versus cells with both GA and at least three DSB foci (B). Scatter plots of percentages per image. Note the striking concurrence of perinuclear GA and nuclear DSB foci within same neurons at D80 in parental C9 and C9-KO as opposed to nearly absent foci of either type in all other conditions. (B, C) Asterisks: highly significant increase in any pairwise comparison with unlabeled conditions, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, N = 60 images from three independent experiments, error bars = SD. All unlabeled conditions (i.e., with no asterisk) were not significantly different among themselves in any pairwise comparison.
