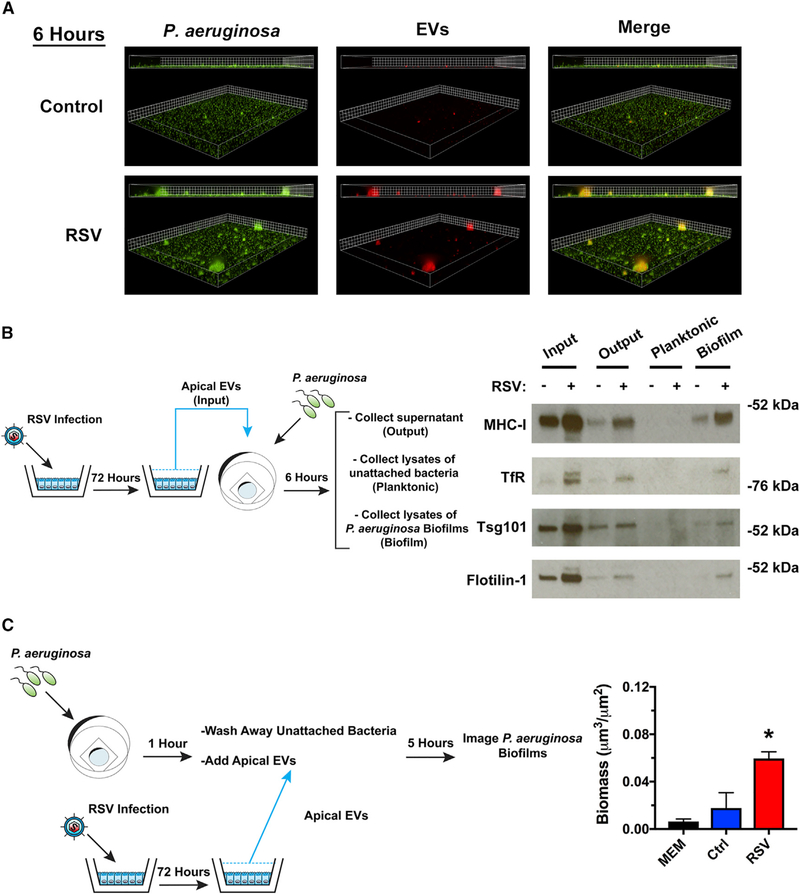
Figure 2. RSV EVs localize with P. aeruginosa biofilms and increase growth of surface-associated P. aeruginosa.
(A) EVs isolated from RSV-infected AECs associate with P. aeruginosa biofilms. AECs were infected with RSV or were mock infected (MEM control) for 48 h. Cells were labeled with CellTracker Deep Red Dye for 45 min, and EVs were collected from dye-labeled cells 24 h later. P. aeruginosa (GFP, green) was grown in the presence of EVs (CellTracker Deep Red, red) for 6 h in static abiotic biofilm assays (grid unit = 5 μM).
(B and C) EVs were isolated from AECs infected with RSV or mock infected (MEM control) for 72 h.
(B) EVs associate with surface associated biofilms in static abiotic biofilm assays, as measured by western blot analysis. EV protein abundance was assessed in (1) EVs before (input) static abiotic biofilm assays, (2) EVs collected after (output) static abiotic biofilm assays, (3) planktonic bacteria collected off the top of static abiotic biofilm assays and washed 2× (planktonic), and (4) in surface-associated bacteria washed 2× (biofilm). The schematic outlines experimental design and the fractions analyzed by western blot analysis.
(C) EVs from RSV-infected AECs increase the growth of surface associated P. aeruginosa. Schematic outlines experimental design. Briefly, P. aeruginosa was given 1 h to attach to glass-bottom dishes. Surface-associated bacteria were grown in the presence of EVs for 5 h in static abiotic biofilm assays.
Control, EVs from mock-infected AECs; RSV, EVs from RSV-infected AECs. For all experiments, n ≥ 3. Data are presented as means ± SD. *p < 0.05 versus control.