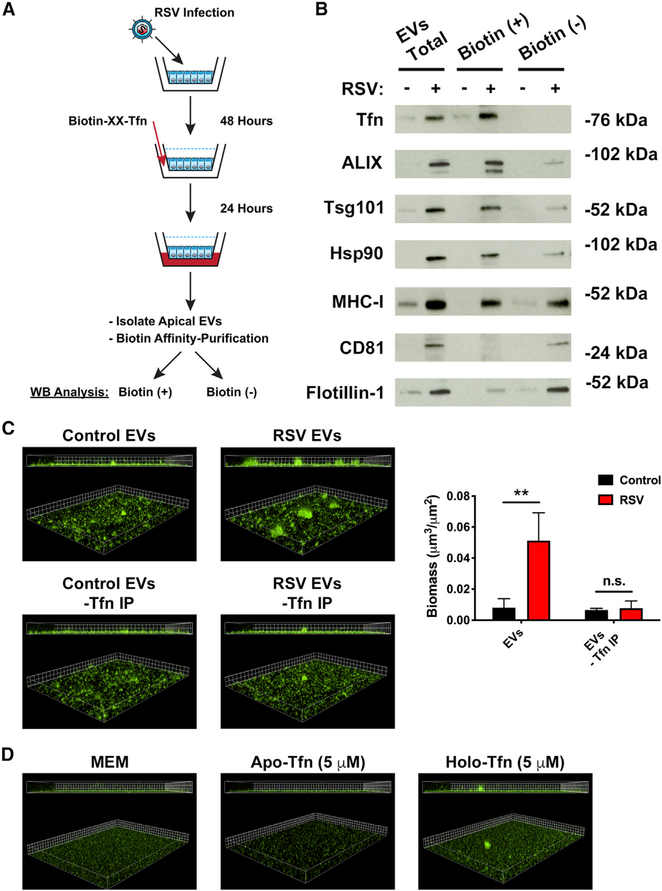
Figure 4. Transcytosed transferrin is loaded on the outside of EVs to enhance P. aeruginosa biofilm growth during RSV infection.
AECs were infected with RSV or mock infected (MEM control) for 48 h. Biotinylated-transferrin was added to the basolateral chamber of RSV or mock-infected AECs at a final concentration of 25 μg/mL. EVs were collected from the apical CM of AECs 24 h later, and biotinylated-transferrin was affinity purified from EV preparations with streptavidin-coated beads. Bead-bound proteins were eluted from the resin (transferrin IP), and supernatant from the streptavidin resin (IP Sup) were separated by SDS-PAGE.
(A) Schematic of experimental design.
(B) Transcytosed transferrin and protein markers of EVs were measured by western blot analysis in transferrin IP (biotin-positive) and IP Sup (biotin-negative) fractions.
(C) P. aeruginosa (GFP) was grown in the presence of EVs in static abiotic biofilm assays after biotin affinity purification to remove transferrin-positive EVs (grid unit = 7.5 μm).
(D) Free, EV-unbound transferrin sources (apo- and holo-transferrin; iron-free and iron-replete, respectively) dissolved in MEM do not promote P. aeruginosa (GFP, green) biofilm growth. Biofilm growth was measured by static abiotic biofilm assays (grid unit = 7.5 μm).
Control, EVs from mock-infected AECs; RSV, EVs from RSV-infected AECs. For all experiments n ≥ 3. Data are presented as means ± SD. *p < 0.05 versus control.