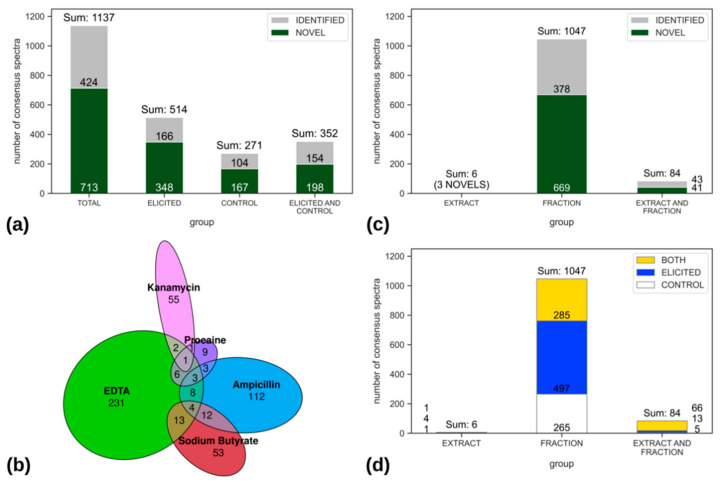
Figure 3.
MS/MS consensus spectra distribution across the working groups reveals that the elicitation and fractionation strategies used for the bacterial chemical library construction increased the number and novelty of the metabolites detected by LC-MS/MS. (a) Distribution of total MS/MS consensus spectra related to [M + H]+ ions linked to bacterial metabolites (spectra related to chromatographic blanks, culture media and elicitors were excluded), in the different bacterial growth conditions: exclusively in the elicited conditions (elicited), non-elicited conditions (control) and in both elicited and control conditions. Bars are colored according to matches with databases (match = identified (grey), unmatched = potentially novel compound (green)). The cut-off for considering a spectrum as identified was MQScore ≥ 0.2, for the UNPD-ISDB (in silico), and MQScore ≥ 0.65, for GNPS (experimental) databases, with the MQScore ranging from 0 (totally dissimilar) to 1 (completely identical). (b) Euler diagram distribution of themetabolites detected exclusively under the elicited conditions: EDTA 10 mM, ampicillin 100 µg/mL, sodium butyrate 50 µM, kanamycin 100 µg/mL and procaine 100 µM. (c) Distribution of the metabolites detected exclusively in crude extracts (extract), fractions and both extract and fraction samples. Bars are color coded according to compound identification in databases—the same criteria used in (a) was applied. (d) Distribution of the metabolites detected in crude extracts, fractions and both extract and fraction samples, colored according to their detection in control (white), elicited (blue) or both (yellow—control and elicited) growth conditions.