Figure 1. Increased proinflammatory cytokines tumor-necrosis factor alpha (TNF), interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) in Gabrg2+/Q390X, a genetic mouse model of epileptic encephalopathy.
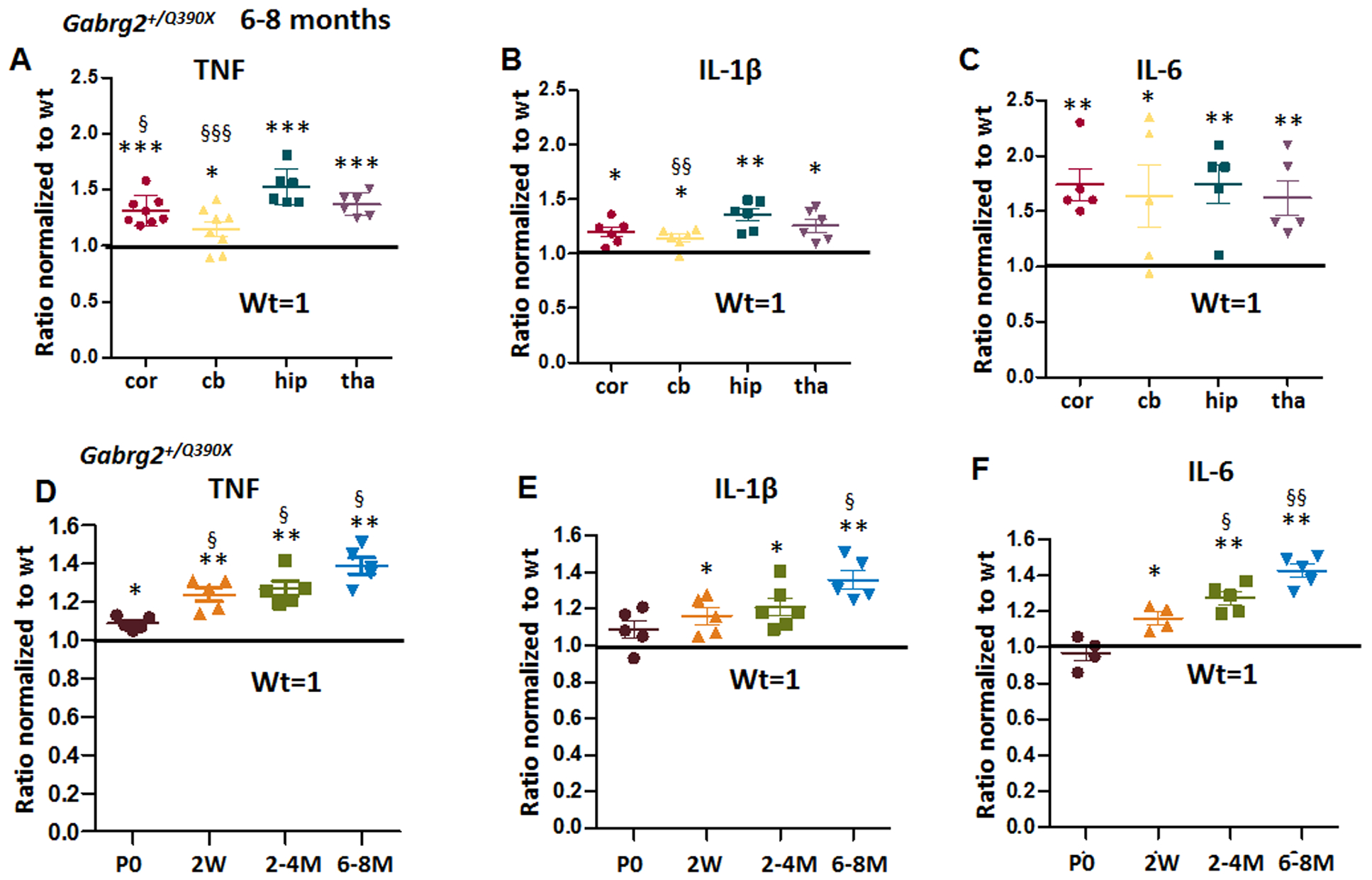
A-C. The brains from 6–8 months old Gabrg2+/Q390X mice were dissected and processed for measurement of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Equal amounts of protein lysates (30μg) from each brain region were determined for cytokines including tumor-necrosis factor alpha (TNF) (A), interleukin 1β (IL-1β) (B) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) (C) with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The measurements in the heterozygotes (het) were normalized to the same brain region of their own wildtype (WT) littermates. D-F. The forebrain cortex from the Gabrg2+/Q390X mice at different ages (P0=postnatal day 0, 2W=2 weeks, 2–4M=2–4 months, 6–8M=6–8 months) were dissected and processed for measurement of TNF (D), IL-1β (E) and IL-6 (F) with ELISA. Equal amounts of protein lysates (30μg) from the mouse cortex of different ages were determined. In D-F, the measurements in the het were normalized to the cortex of their own wildtype littermates. (In A-F, *p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 vs wt, In A-B, § P< 0.05; §§ P< 0.01 §§§ P< 0.001 vs hip in het; in D-F, § P< 0.05; §§P< 0.01 vs P0). Data were presented as mean ± S.E.M. In A-C, N=5–8 mice. In D-F, N=4–6 mice.
