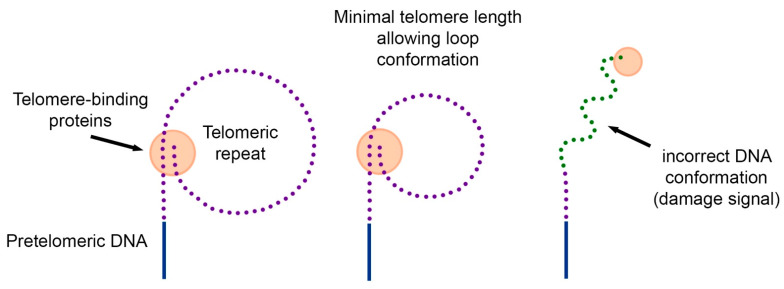
Figure 2.
The hypothesis of the loop structure of telomeres. Telomeric DNA together with telomere-binding proteins can form loops. Due to the restriction of free rotation of DNA and interaction with various proteins, the DNA in the loop has a strained conformation. When telomeric DNA is shortened, there comes a point when the length of the telomeric repeat does not allow the loop to form. The telomeric end of the DNA acquires a free conformation, which is perceived by the cell as a signal of damage. As a result, the mechanism of replicative cell senescence is triggered.