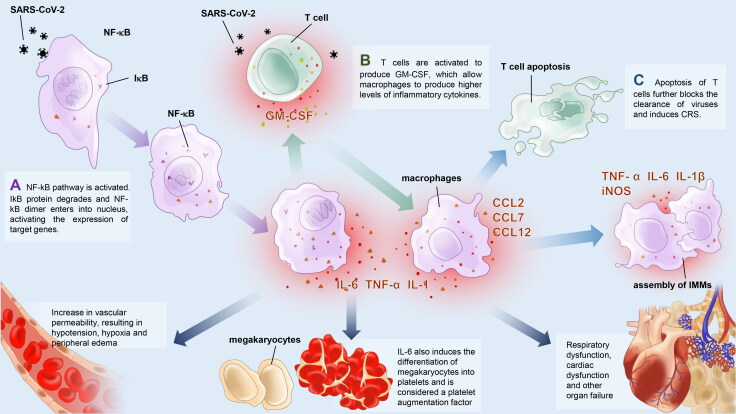
Figure 1.
IL-6 and GM-CSF in NF-?B pathways. A. The N and S protein of SARS-CoV-2 interact with the NF-?B complex, leading to phosphorylation and degradation of I?B, and to the release of NF-?B dimers and translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. The NF-?B dimers further bind to DNA binding sites and upregulate the expression of target genes such as IL-6, TNF-? and GM-CSF. B. GM-CSF further stimulates CD14 + CD16+ monocytes to produce higher levels of IL-6 and other inflammatory cytokines. C. By promoting the production of other cytokines and chemokines, differentiation of monocyte and macrophage, attraction of other immune cells and inhibiting Treg cells, IL-6 may play an important role in apoptosis of T cells and development of CRS.