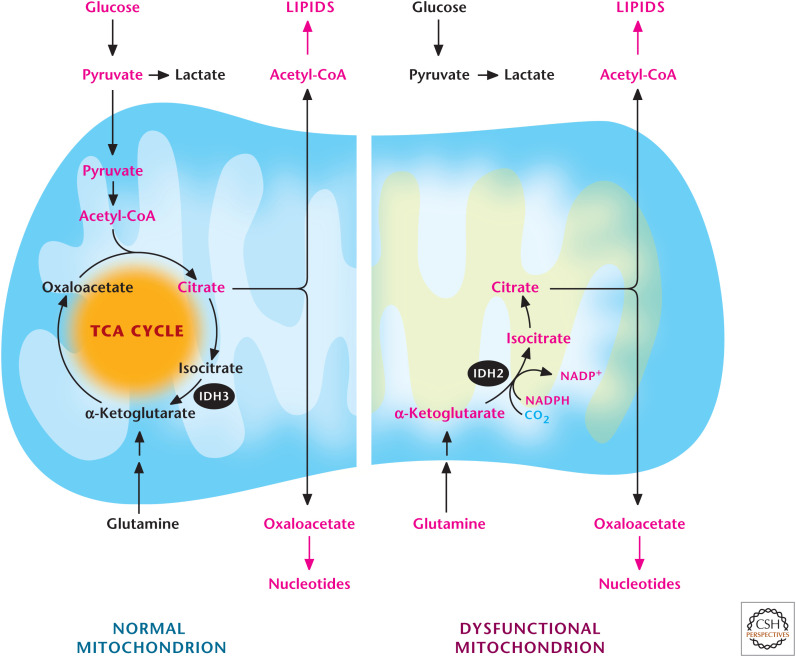
Figure 12.
Glutamine-dependent reductive carboxylation. Cells that have functional mitochondria can use glutamine to generate α-ketoglutarate to produce OAA and use pyruvate to generate acetyl-CoA. OAA and acetyl-CoA generate citrate, which can be exported into the cytosol to produce de novo lipids and nucleotides. Cells that have dysfunctional mitochondria due to loss-of-function mutations of proteins in the TCA cycle after the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase step or in the ETC cannot oxidize pyruvate into acetyl-CoA. They convert glutamine into α-ketoglutarate, which subsequently becomes citrate through a reverse IDH2-dependent reaction.