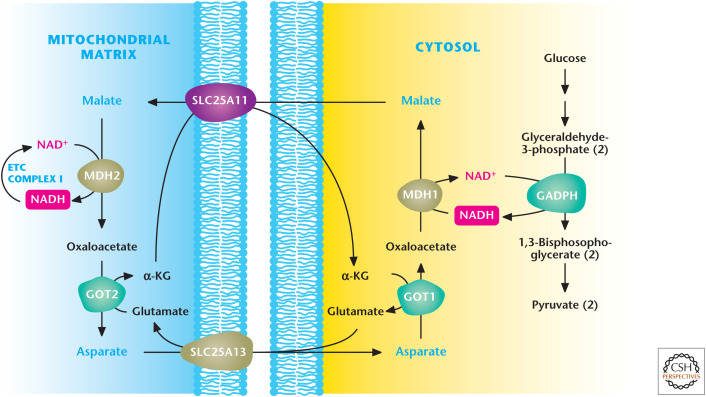
Figure 7.
Malate–aspartate shuttle. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) generates NADH during glycolysis. NADH can be regenerated to NAD+ to allow glycolysis to continue by the conversion of oxaloacetate (OAA) to malate by cytosolic malate dehydrogenase 1 (MDH1). Subsequently, malate is transported by the SLC25A1 transporter into the mitochondrial matrix, in which it is converted back to OAA coupled with NAD+ conversion into NADH. The ETC complex I converts NADH into NAD+ to keep malate dehydrogenase 2 functioning continuously. The mitochondrial OAA is converted into aspartate by aspartate aminotransferase 2 (GOT2) and, subsequently, transported into the cytosol, where aspartate can be converted back into cytosolic OAA by aspartate aminotransferase 1 (GOT1) for the shuttle to continue. α-KG, α-ketoglutarate. (Adapted with permission of themedicalbiochemistrypage, LLC.)