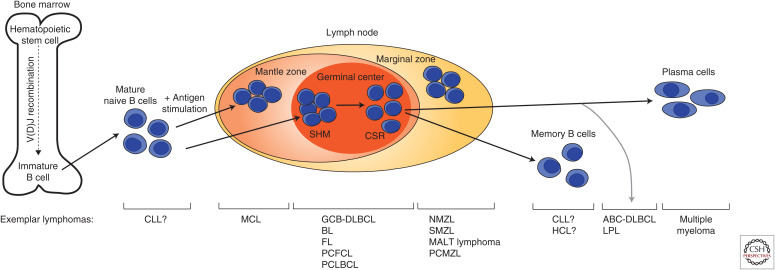
Figure 1.
B-cell development. Progenitor B cells undergo V(D)J recombination in the bone marrow before exiting at the immature B-cell stage. Upon antigen stimulation, mature B cells undergo somatic hypermutation (SHM) and class-switch recombination (CSR) in the germinal center before undergoing terminal differentiation into plasma or memory B cells. Examples of lymphomas that can arise at each B-cell stage are noted. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma; GCB-DLBCL, germinal center B-cell diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; BL, Burkitt lymphoma; FL, follicular lymphoma; PCFCL, primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma; PCLBCL, primary cutaneous large B-cell lymphoma; NMZL, nodal marginal zone lymphoma; SMZL, splenic marginal zone lymphoma; MALT, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue; PCMZL, primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma; HCL, hairy cell leukemia; ABC-DLBCL, activated B-cell like DLBCL; LPL, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma.