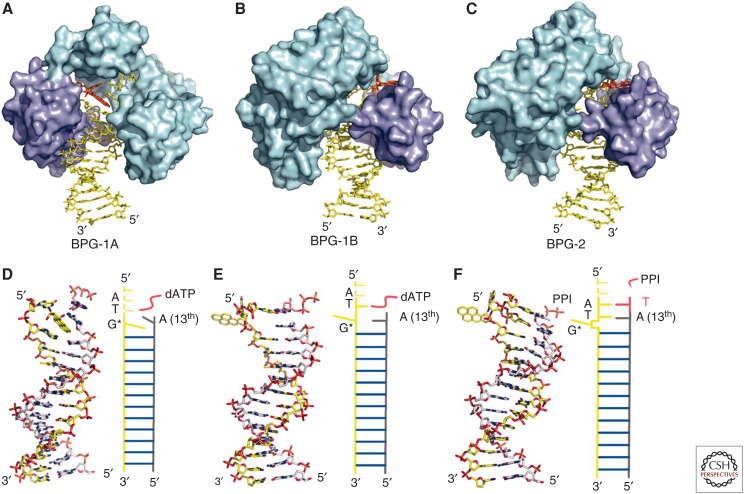
Figure 10.
The hydrophobic BP-DNA adduct prefers to intercalate between the hydrophobic bases of the DNA double helix (A,D). However, a hydrophobic pocket peculiar to the Y-family DNA polymerases flips the BP-DNA adduct out of the double helix (B,C,E,F), thereby permitting bypass synthesis. (Reprinted, with permission, from Bauer J, et al. 2007. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104: 14905–14910, © National Academy of Sciences, USA.)