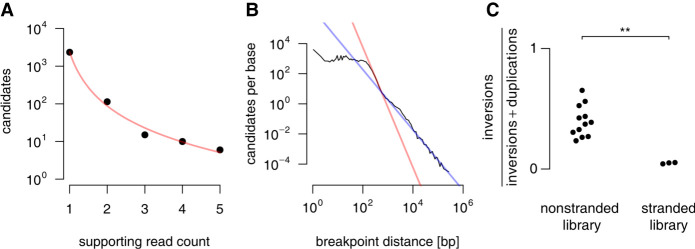
Figure 6.
Covariates used to estimate the level of background noise. One of Arriba's artifact filters removes candidates with fewer supporting reads than the estimated level of background noise. For this purpose, Arriba calculates several covariates that correlate with the level of background noise. (A) Arriba assumes a polynomial relationship between the noise level (unfiltered candidates) and their number of supporting reads. The data shown here are based on the highly expressed housekeeping gene GAPDH in the MCF-7 cell line (SRA accession ERR358487). (B) The figure shows the number of unfiltered candidates as a function of the breakpoint distance averaged over all genes in the MCF-7 cell line. Artifacts tend to have breakpoints in close proximity as evidenced by a sharp increase in the number of candidates with decreasing distance. Arriba fits two models depending on whether the breakpoints are closer or further apart than 400 bp (red and blue lines, respectively). (C) The library preparation method can affect the proportions of artifacts. For example, the samples from Heining et al. (2018) are a mixture of stranded and nonstranded libraries. The stranded libraries are enriched for duplications compared with the nonstranded libraries (two-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test, P-value = 0.0044).