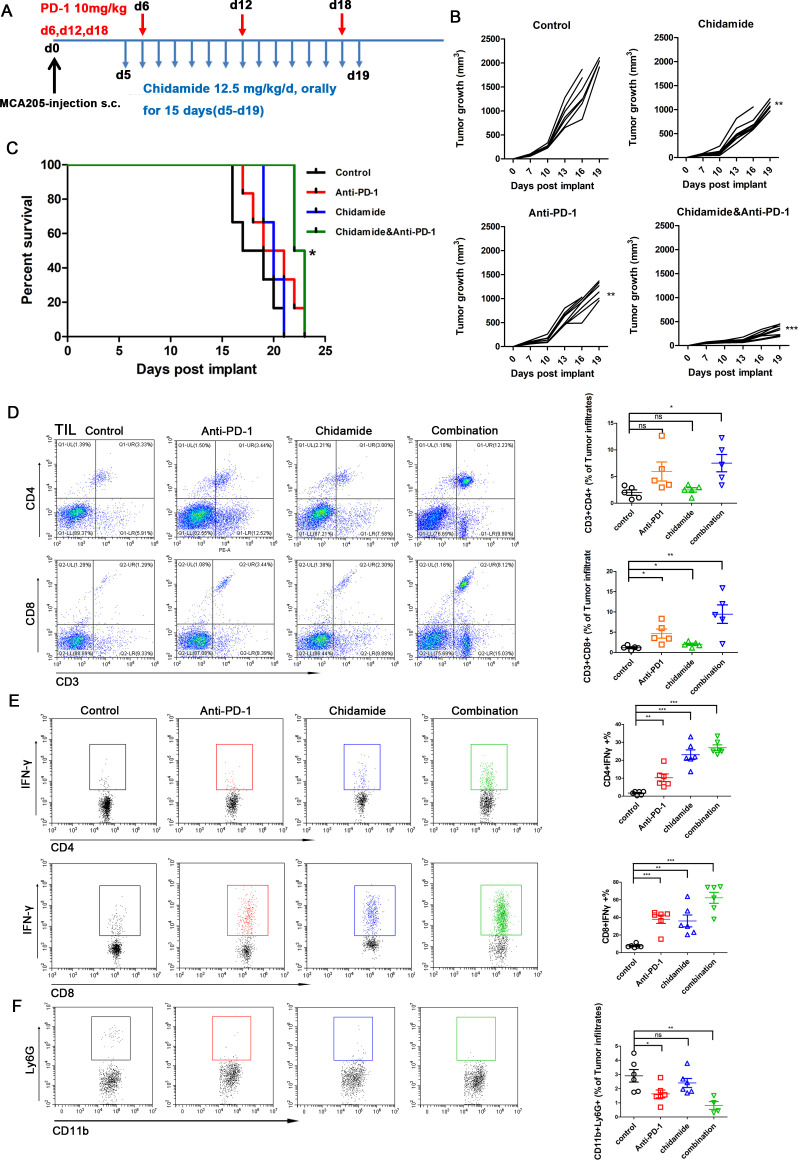
Figure 4.
Combining chidamide with PD-1 blockade in vivo results in enhanced survival and leads to increased antitumor activity compared with single therapy and untreated group. C57BL/6 mice were inoculated subcutaneously with MCA205 sarcoma cells. (A) A schematic of treatment for C57BL/6 mice bearing subcutaneous MCA205 tumors. (B) Individual tumor volumes for each group was measured over time (n=8 per group). (C) The survival curve of combination group was significantly different from the control group. Log rank test of survival curve differences were p<0.05. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001. (D) After treatment, different group tumors performed FACS to determine CD4 (CD3+CD4+) and CD8 (CD3+CD8+) in total viable cells. combination therapy leads to dramatic increase of CD4 (CD3+CD4+) and CD8 (CD3+CD8+) percentages of tumor infiltrated cells compared with control group. (E) IFN-γ production in CD4+ and CD8+ TILs in each group. Combination treatment increased the IFN-γ production in CD4+ TIL and CD8+ TIL. (F) CD11b+Ly6G+ percentage cells were attenuated by treated with chidamide and anti-PD-1 most significantly. *P<0.05. **p<0.01. ***p<0.001. TIL, tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte.