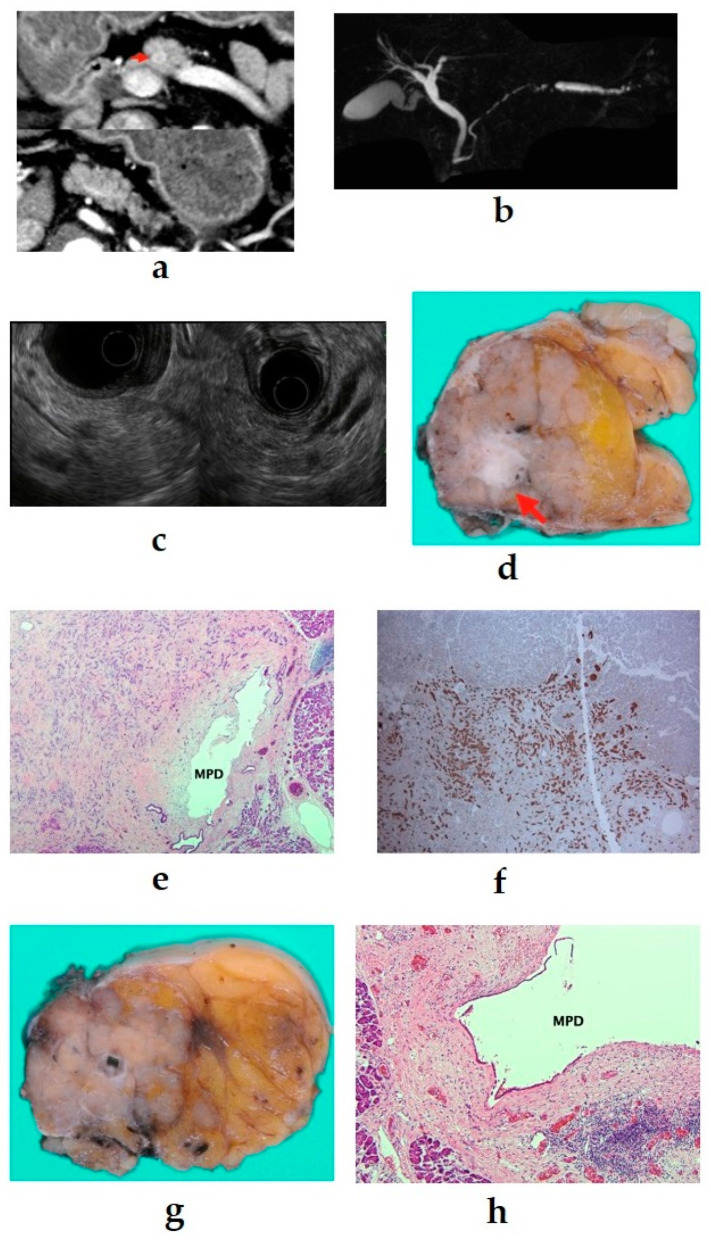
Figure 4.
(a) Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT): a mass lesion with early hyperenhancement is seen in the pancreatic body (red arrow), but there are no other obvious lesions. (b) Magnetic resonance imaging: the main pancreatic duct (MPD) in the pancreatic body is extensively narrowed, and the caudal duct is dilated. (c) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS): a circular hypoechoic mass in the pancreatic body. Pancreatic duct stenosis is observed even in the absence of mass. (d–f) 6-mm neuroendocrine neoplasm G1 (red arrow), serotonin positive, with stromal fibrosis (40×). (g,h) Pancreatic duct stenosis due to stromal fibrosis upstream of the tumor (40×).