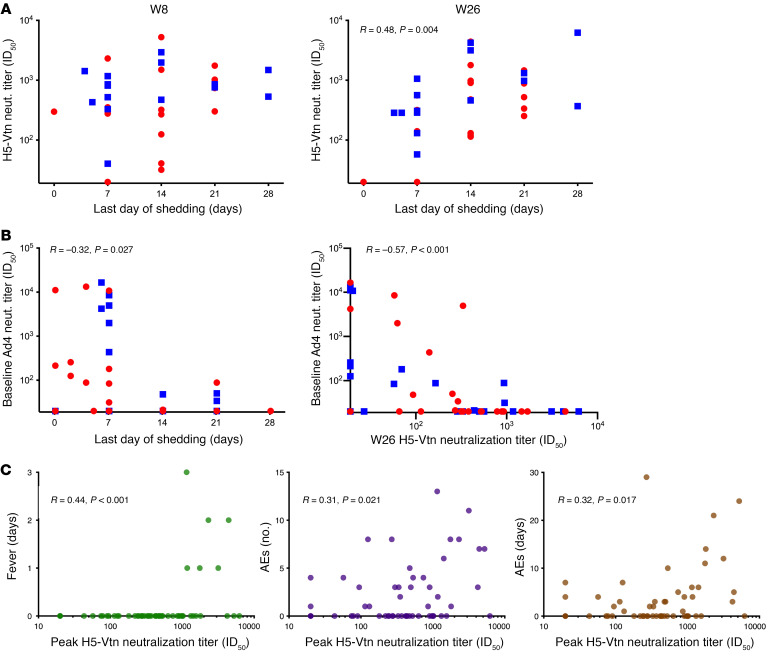
Figure 3. Clinical correlates of anti-H5–neutralizing antibody titers.
(A) The correlation between H5-neutralizing antibody titers 8 weeks (left, n = 32) and 26 weeks (right, n = 33) after vaccination and the last day of viral shedding detected was assessed for participants from the tonsillar (blue squares) and intranasal (red circles) groups who had a 4-fold increase in Ad4-neutralizing antibody titers after vaccination. Significance was determined by Spearman’s rank method. Only significant P values are shown. (B) The correlation between Ad4-neutralizing antibody titers at baseline and the last day of detectable viral shedding (left, n = 48) and peak H5-Vtn neutralization titers (right, n = 49) was assessed by the Spearman’s rank method. Symbols are as in A. Vaccinees who did not seroconvert to Ad4 are included for the purpose of this analysis. (C) The correlations between peak H5-neutralizing antibody titers after vaccination and the duration of related fever (days, left), the total number of participants with related AEs (middle), and the duration of related AEs (days, right) was assessed among vaccine recipients in the oral, tonsillar, and intranasal arms (n = 56; participants with matching AEs and H5-neutralizing antibody titers are shown). The Spearman’s rank method was used to determine significance.