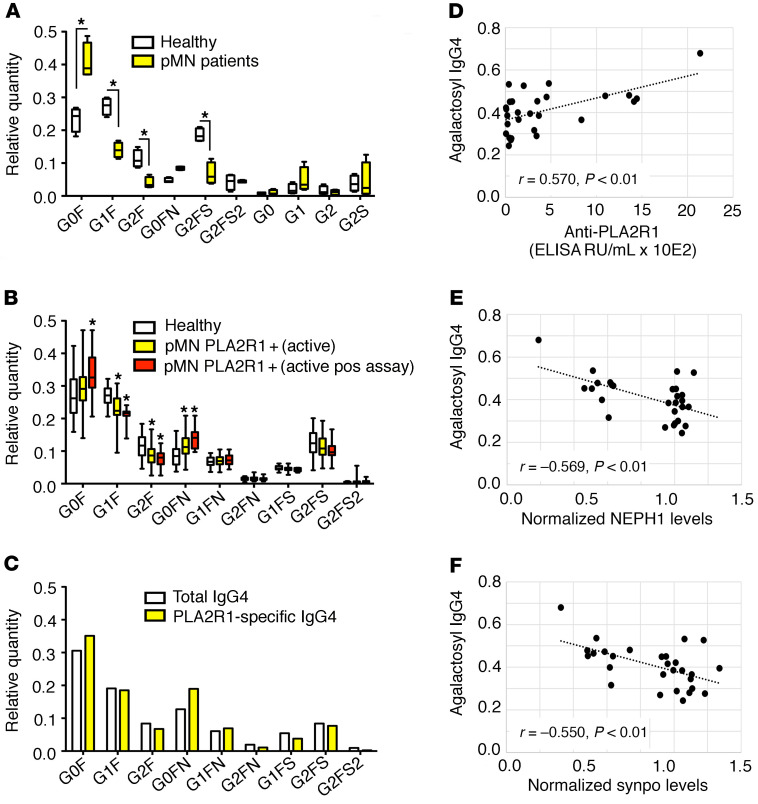
Figure 6. IgG4 antibodies from patients with pMN exhibit an altered glycosylation pattern.
(A) Preliminary analysis of the glycosylation pattern of IgG4 purified from sera of pMN patients and controls (n = 4 each). The box shows median and IQR, the whiskers minimum and maximum values, *P < 0.05 unpaired t test. (B) Analysis of the IgG4 glycosylation pattern using nanoLC-MS of glycopeptides in an extended cohort. The entire cohort of PLA2R1-positive pMN patients with active disease (n = 31, for definition of active disease see Supplemental Table 2) and patients with a positive result (i.e., a statistically significant decrease of synaptopodin and NEPH1 by more than 25% in 3 independent experiments) in the cellular complement assay (n = 10) were compared with age- and sex-matched healthy controls (n = 39). The box shows median and IQR, the whiskers minimum and maximum values, *P < 0.05 adjusted for residual confounding by differences in age and sex. (C) PLA2R1-specific IgG4 was purified from the pooled IgG4 fraction of 5 pMN patients (with anti-PLA2R1 levels of 451–1443 RU/mL) and the glycosylation pattern was compared with total IgG4 from these patients. (D) Correlation of the fraction of agalactosyl IgG4 (G0F + G0FN/total IgG4) with anti-PLA2R1 antibody levels, (E) with synaptopodin, and (F) with NEPH1 levels after exposure to patient sera and complement in all patients with active pMN. r, Pearson’s correlation coefficient. See Supplemental Figure 16 for an explanation of the glycosyl side chain nomenclature.