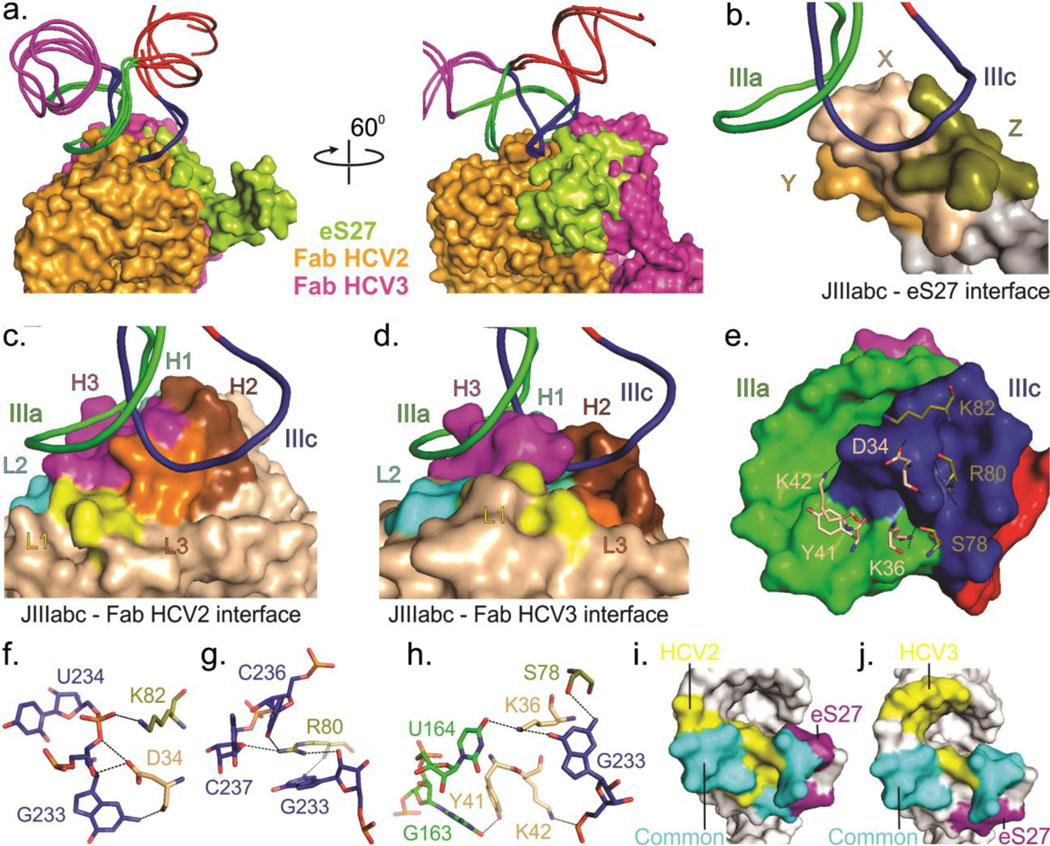
Fig. 4.
Comparison of binding interfaces of JIIIabc – HCV2, JIIIabc – HCV3 and JIIIabc – eS27 complexes. (a) Superposition of the JIIIabc portion of the JIIIabc – HCV2, JIIIabc – HCV3 (crystal structures) and JIIIabc – eS27 (3.9-Å cryo-EM model, PDB code: 5A2Q)25 complexes. Molecular surfaces of the Fabs HCV2, HCV3 and protein eS27 are shown in orange, purple and lime-green colors. (b-d) Overall view of the binding interfaces for JIIIabc – eS27 (b), JIIIabc – HCV2 (c) and JIIIabc – HCV3 (d) complexes, highlighting that these proteins recognize a common epitope (IIIa and IIIc sub-domains) within the JIIIabc RNA. X, Y and Z in eS27 molecular surface are arbitrary assignments. (e) Molecular surface of the JIIIabc interface (3.9-Å cryo-EM model) and the eS27 residues that are involved in binding interactions with the RNA epitope. (f-h) Specific interactions between the RNA epitope and the eS27 residues. The dashed lines reflect hetero-atoms within hydrogen bonding distance. (i-j) Molecular surfaces of the JIIIabc showing a common and different recognition surfaces within the RNA epitopes by HCV2 and eS27 (i) and by eS27 and HCV3 (j). Unless specified, all figures and the labels are colored analogously for facile comparison.