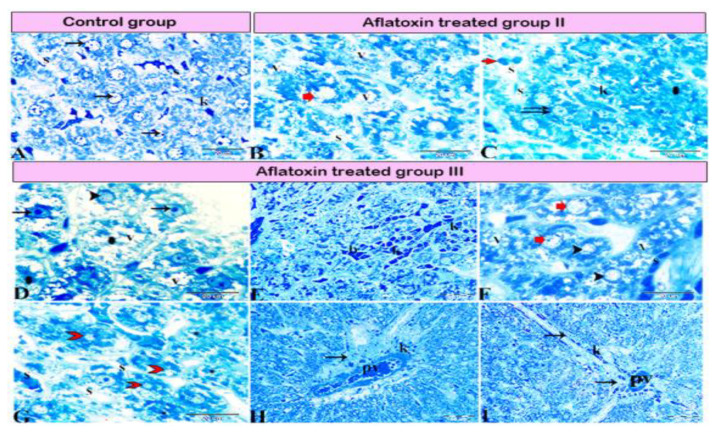
Figure 4.
Photomicrograph of a semi-thin section stained with Toluidine blue. (A) Normal hepatocytes (arrows) with narrow blood sinusoids (S) in between; note the presence of Kupffer cells (K) in the sinusoids. (B,C) Aflatoxin B1-treated rat from group II. (B) hepatocellular vacuolar degeneration (V), dilated sinusoids (S), and presence of hepatic megalocytes (red arrow). (C) Binucleated hepatocytes (double arrow), incomplete mitotic division (red arrow), area of necrosis (star), dilated sinusoids (S), and marked Kupffer cell (K) proliferation inside the lumen. (D–I) AFB1-treated rat from group III. (D) Severe hepatocellular vacuolar degeneration (V), some hepatocytes with basophilic bodies (arrows), vesicular nuclei (arrowhead), and other hepatocytes showing necrosis with karyolitic nuclei (stars). (E) Sinusoids dilated and filled with blood (b) and marked Kupffer cell (K) proliferation inside the sinusoidal lumen. (F) Hepatocellular vacuolar degeneration (V), presence of hepatic megalocytes (red arrows), and necrotic hepatocytes (arrowheads). (G) Hepatocellular necrosis (red arrowhead) with notable areas of cellular necrosis and lost detail (star). (H) Severe periportal fibrosis (arrow), with the portal vein (PV) engorged with blood, severe fibrosis, and marked Kupffer cell proliferation (K). (I) Marked fibrosis around the portal vein (PV), which diffused inside the hepatic lobule forming tracts of fibrosis (arrows).