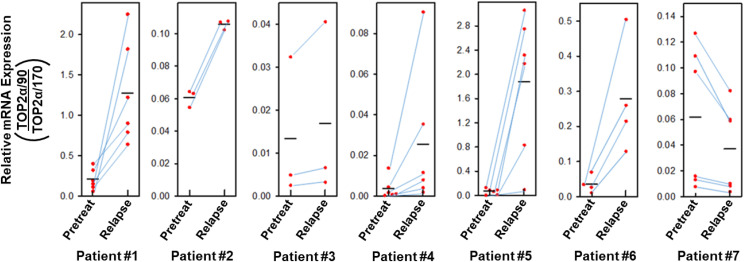
Fig. 2.
Effects on TOP2α/90:TOP2α/170 mRNA ratios in patients with AML upon post-therapy relapse. Total RNA samples were isolated from blast cells obtained from patients newly diagnosed with AML and the same patients at relapse, after receiving TOP2α-targeting therapy. qPCR experiments were performed utilizing TaqMan hydrolysis probes specific for TOP2α/170 and TOP2α/90 mRNAs as described in Materials and Methods and as used previously (Kanagasabai et al., 2017). From each patient’s samples (pretreatment and at relapse), cDNAs were generated in parallel from isolated RNAs by reverse transcription, and qPCR reactions were subsequently performed in parallel using a common master reaction mix. In addition, these evaluations were repeated on separate days by generation of cDNAs with subsequent qPCR reactions performed from each pair of patient’s samples. The ratio of TOP2α/90:TOP2α/170 mRNA pretreatment and after relapse was calculated and plotted as coordinate plots with point-line-point connections for each pair of evaluations for each patient. For patient #1, one of the sets of values connected by point-line-point for pretreatment (0.4) and relapse (0.9) were indicated in a previous publication (Kanagasabai et al., 2018). The black horizontal bars represent the mean values from repeated paired measures. Evaluation of the mean values for TOP2α/90:TOP2α/170 mRNA ratios pretreatment and after relapse for all seven patients indicated an average 4.01-fold increase that was statistically significant after performing a paired t test on log transformed values; P = 0.036 [95% CI (1.14, 14.16)].