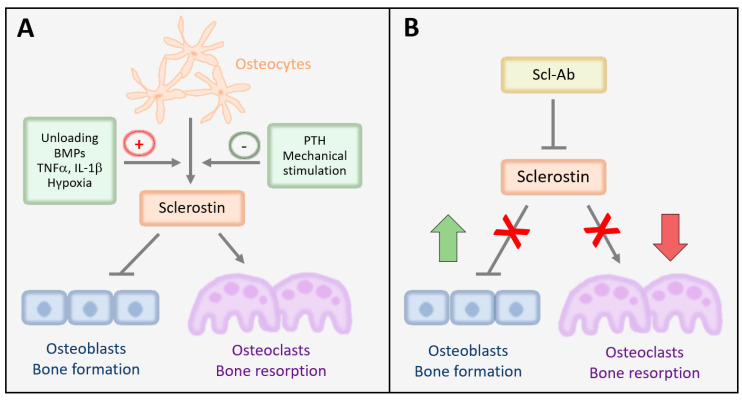
Figure 1.
Regulation of sclerostin and its effects on bone cells and mode of action of sclerostin antibodies. (A) Regulation of sclerostin and its effects on bone cells. Sclerostin is produced mainly by osteocytes and is negatively regulated by mechanical loading and parathyroid hormone (PTH) and positively by unloading, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL-1β), and hypoxia. Sclerostin inhibits osteoblastogenesis and thus bone formation and stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. (B) Mode of action of sclerostin antibodies. Sclerostin-antibodies (Scl-Ab) neutralize sclerostin and thereby stimulate bone formation and inhibit bone resorption, producing a large anabolic window.