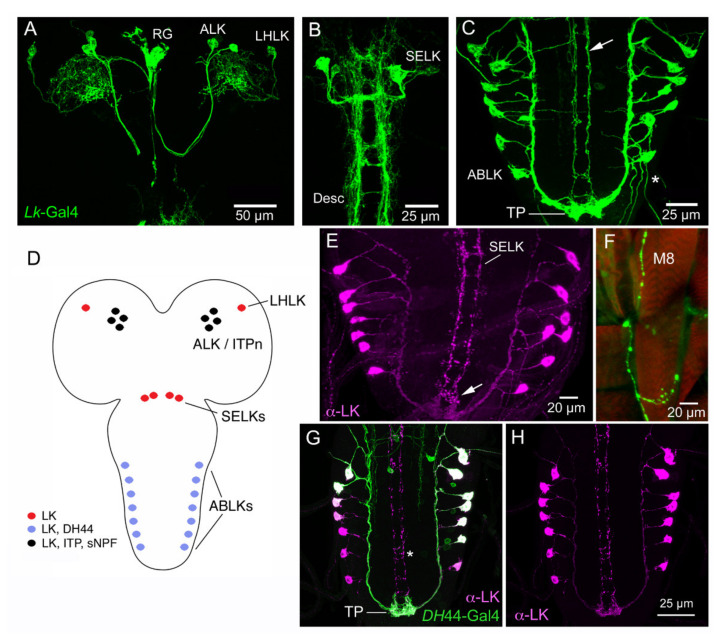
Figure 1.
Expression of leucokinin (LK) and other peptides in the CNS of larval Drosophila. (A) Larval brain with Lk-Gal4 expression in LHLK (lateral horn LK) and ALK (anterior LK) neurons. The ALKs have axon terminations in the ring gland (RG). (B) SELK (subesophageal LK) neurons of the larval brain/ventral nerve cord with their descending axons (Desc). (C) The abdominal leucokinin neurons (ABLKs) and axons of SELKs (arrow). Note the terminal plexus neuropil (TP) with axonal processes of both ABLKs and SELKs. (D) Schematic of the LK-expressing cell bodies. Colors indicate the different peptides expressed in the neurons. (E) LK immunolabeling of ABLKs and SELK axons. The arrow indicates the terminal plexus. (F) Axon termination of an ABLK on body wall muscle 8 (M8). (G,H) The ABLKs, but not SELKs (asterisk), co-express LK and diuretic hormone 44 (DH44). Images in Figure 1 are modified and rearranged from [37,96], with permission from publishers.