Figure 1.
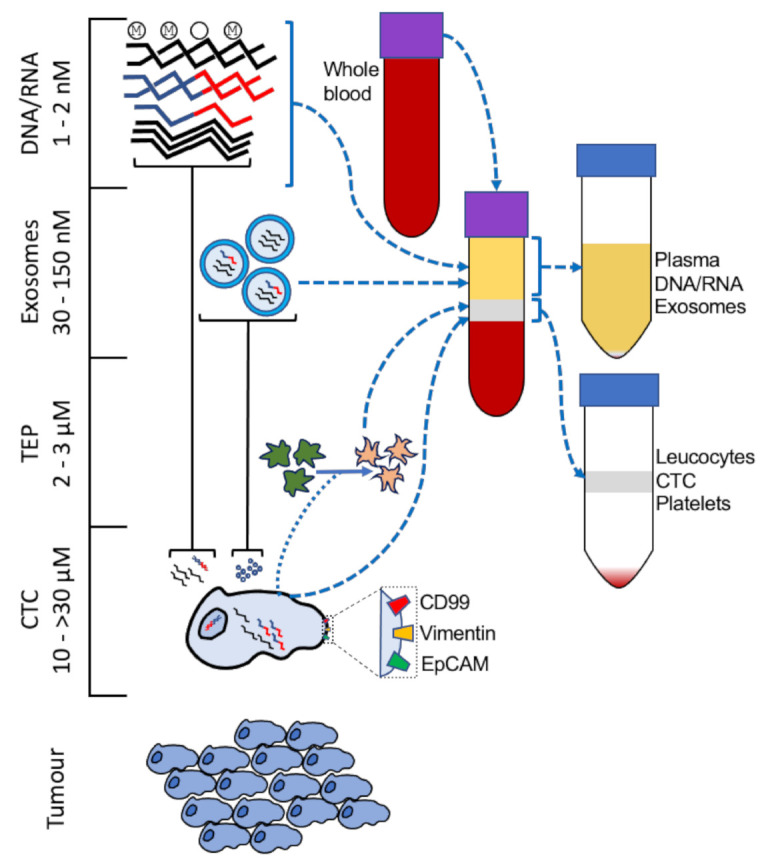
Tumour components present in liquid biopsy. Enrichment of circulating tumour cells (CTC), tumour-educated platelets (TEP), exosomes, and free polynucleotides is achieved by centrifugation and density separation. Whole blood from patients may be centrifuged to separate the plasma layer and the ‘buffy coat’ (leucocytes, platelets, and CTC) from the denser granulocyte/erythrocyte layer. RNA from CTC or cfRNA may be of the fusion gene (e.g., EWSR1-FLI1 [1]) or, as with TEP [19] and exosomal RNA [20], differentially expressed upon relapse. cfDNA from tumours may be differentially methylated [21] and/or contain chromosomal translocations [22]. Surface markers (e.g., CD99, Vimentin, EpCAM) may be detected by FACS or IHC [23,24,25].
