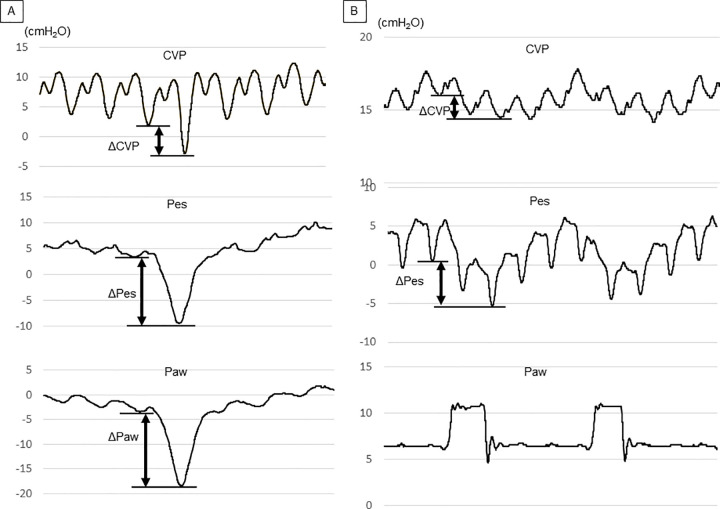
Fig 1.
Pressure waveforms for CVP, Pes, and Paw during an occlusion test (A) and during assisted and unassisted spontaneous breathing under ventilatory support (B). (A) During an occlusion test, the three waveforms fluctuate in a similar manner. ΔPaw should be close to ΔPes during an occlusion test, provided that the position of the esophageal balloon catheter is correct. In Fig 1, for example, ΔPes was 12.9 cmH2O and ΔPaw was 15.2 cmH2O, leading to a ΔPes to ΔPaw ratio of 0.85. The ratio of ΔPaw to ΔCVP obtained during the occlusion test was expressed as “k.” (B) ΔCVP and ΔPes were measured during assisted spontaneous breathing under mechanical ventilation. The ΔPpl was then calculated by multiplying k of the same patient by ΔCVP. CVP: central venous pressure; ΔCVP: change in central venous pressure; Pes: esophageal pressure; ΔPes: change in esophageal pressure; Paw: airway pressure; ΔPaw: change in airway pressure; ΔPpl: change in pleural pressure.