Figure 5.
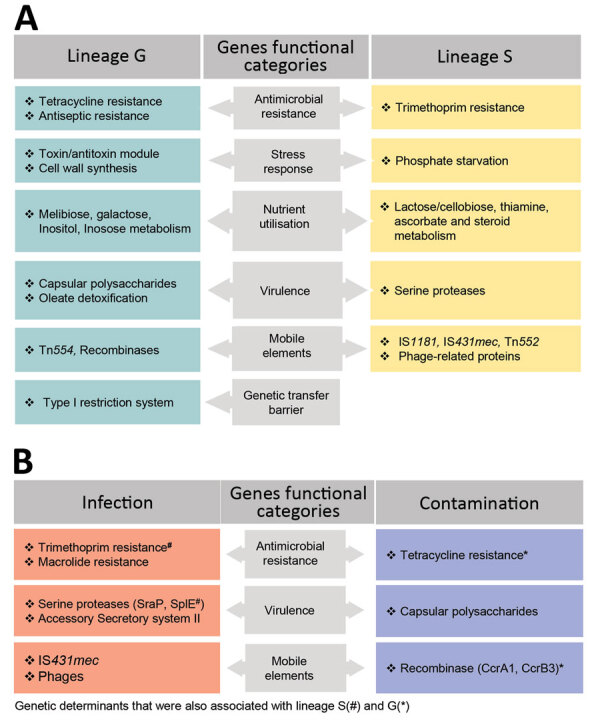
Genetic determinants that contribute to the distinction of clonal lineages and lifestyle of Staphylococcus saprophyticus. The graph displays determinants that contribute (A) and mediate (B) adaptation of S. saprophyticus to either infection or contamination. We used the genome-wide association study (GWAS) method to identify genetic factors by using 2 association comparisons: lineage G versus lineage S and human infection versus surface contamination. We used the pairwise comparison and included a core-SNP phylogenetic tree without recombination to remove the lineage effect in the analysis. Hits with Benjamini Hochberg corrected p<0.05 and odds ratio >1 were considered statistically significant. We grouped the identified genes into biologic functions based on gene annotation predicted by Prokka (https://vicbioinformatics.com/software.prokka.shtml). Some genetic factors that were associated with infections and contamination also were associated with the lineages despite subjecting the GWAS to lineage correction.
