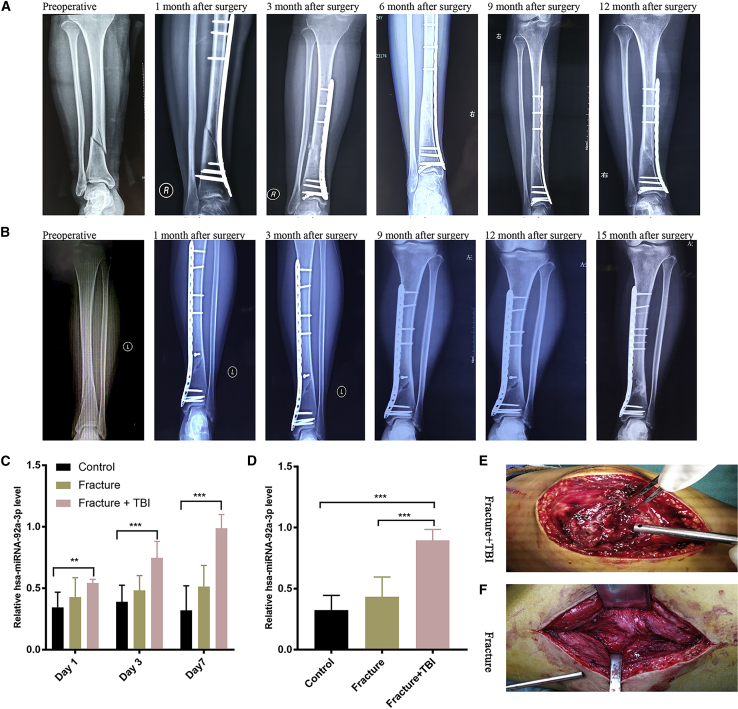
Figure 1.
miRNA-92a-3p expression is elevated in the plasma and callus of patients with concomitant extremity fractures and brain trauma
(A) 34-year-old female patient with concomitant fracture of the distal tibia and brain trauma. X-rays of the anterior and posterior tibia and fibula at 1 week before surgery, and 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, and 12 months after surgery. (B) 32-year-old female patient with fracture of the distal tibia. X-rays of the anterior and posterior tibia and fibula at 1 week before surgery, and at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, and 15 months after surgery. (C) miRNA-92a-3p plasma expression. RT-PCR showed that the level of miRNA-92a-3p expression in the plasma of the concomitant fracture and traumatic brain injury (TBI) group was significantly higher than that of the other two groups on day 1, day 3, and day 7 since admission. (D) miRNA-92a-3p callus expression. RT-PCR results showed that the expression level of miRNA-92a-3p in the callus of the concomitant fracture and TBI group was significantly higher than that of the other two groups. (E and F) In the second week after injury, patients with concomitant fracture and TBI were more susceptible to callus formation than those with isolated fractures. N = 10; data are presented as mean ± SD (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; # no significance).