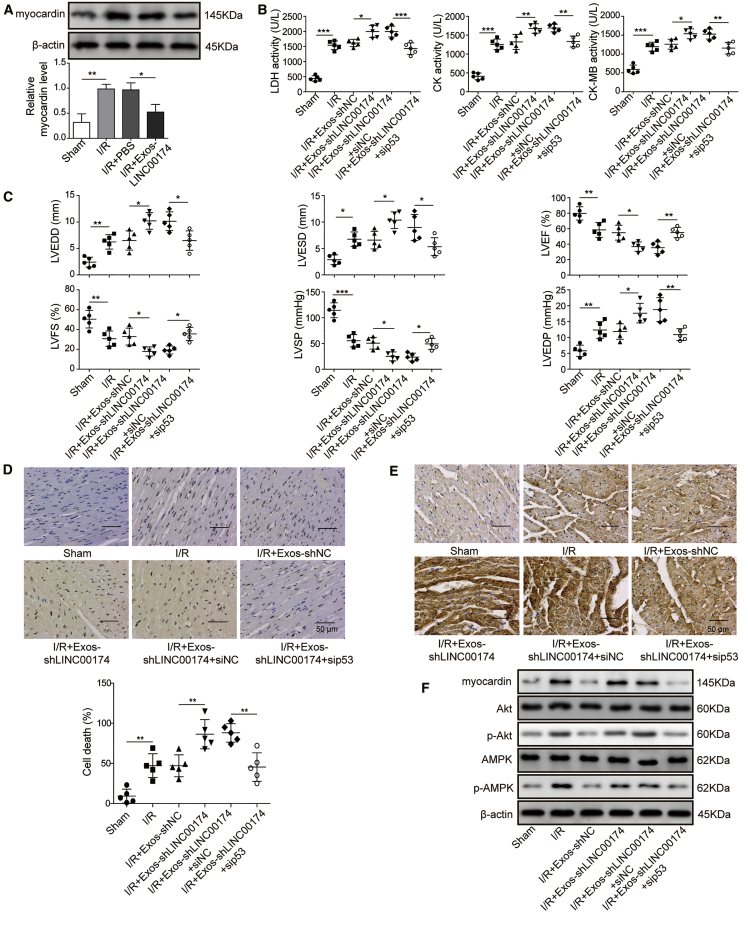
Figure 8.
p53 and myocardin-mediated myocardial I/R injury was modulated by LINC00174 in vivo
(A) I/R-induced myocardial injury mice were treated as indicated; n = 5. The expression level of myocardin in mouse primary myocardial cells was measured 24 h later by western blotting (upper panel) and qRT-PCR (lower panel). β-Actin was used as the loading control in western blotting. GAPDH was used as the normalization control in qRT-PCR.
(B–D) Mice were treated as indicated. The mice were subjected to I/R treatment 4 h later. Sham group mice were not treated by I/R; n = 5.
(B) The activity of LDH, CK, and CK-MB in mice serum was measured by commercial kits.
(C) Key parameters were tested by color Doppler echocardiography to reflect the injury status of myocardium in mice.
(D) The apoptosis of myocardial cells was determined by TUNEL assay; the representative images were displayed in the upper panel, and the statistic of cell death was shown in the lower chart. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(E) The expression level of LC3 in myocardial cells was examined by immunohistochemical staining. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(F) The expression of autophagy-related proteins and the activation of Akt and AMPK pathways in myocardial cells was measured by western blotting; β-actin was used as the loading control.
(A–F) The data represented 1 of 3 independent experiments. (A–D) Data were represented as means ± SDs. p values were determined by 1-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.