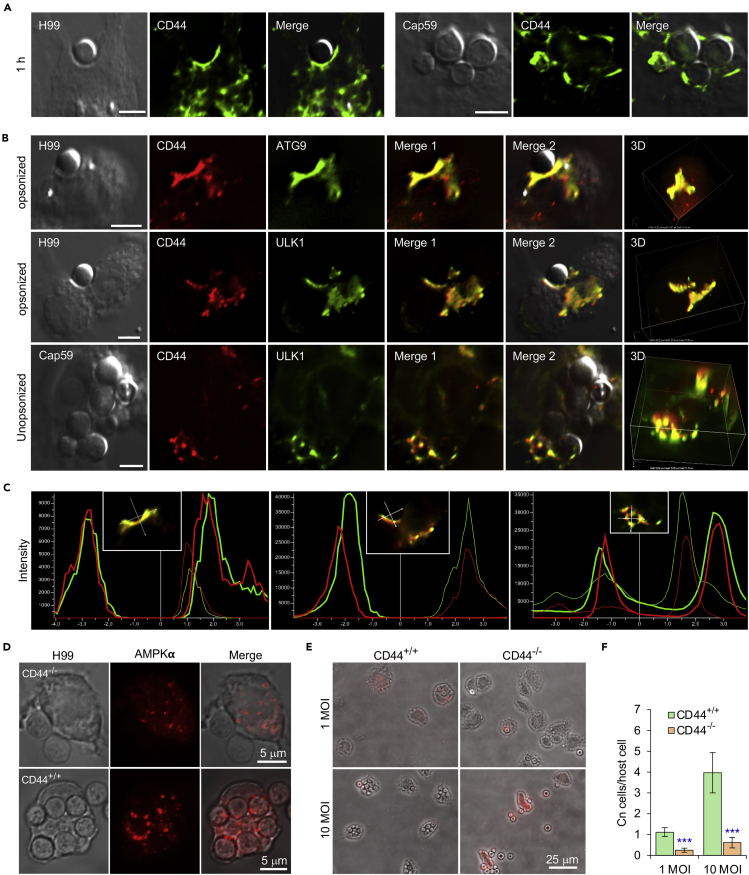
Figure 2.
Host-associated CD44 is required for Cn host cell internalization
(A) Recruitment of host CD44 to nascent CnCVs that contained the wild-type (WT) strain H99 (leaf panel) or acapsular mutant strain cap59 (right panel) of Cn. At 1 h.p.i., host cells were fixed, permeabilized and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies directed against the indicated host proteins. The antibody-stained samples were then subjected to confocal microscopy image analysis. Bars: 5 μm.
(B) Colocalization of CD44 with the indicated AIC components in the vicinity of nascent CnCVs in host cells infected with the indicated Cn strains. Bars: 5 μm.
(C) The fluorescence intensity profile of CD44 (red) and AIC components (ATG9 or ULK1) (green) along the two crossed white lines shown in the insets from (B, Merge 1).
(D) AMPK recruitment to nascent CnCVs in CD44 knockout (KO, CD44−/−) and WT (CD44+/+) bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) at 3 h.p.i.
(E and F) Cn internalization in CD44 WT and KO BMDMs infected by Cn H99 (1 or 10 MOI) assessed using image analysis approaches (E) and corresponding quantification (F) at 3 h.p.i. Data represent the means ± standard error of mean (SEM) from three independent experiments. ∗∗∗: significance at p < 0.001.