Figure 4. Hypothesized Role of Exosomes in SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis.
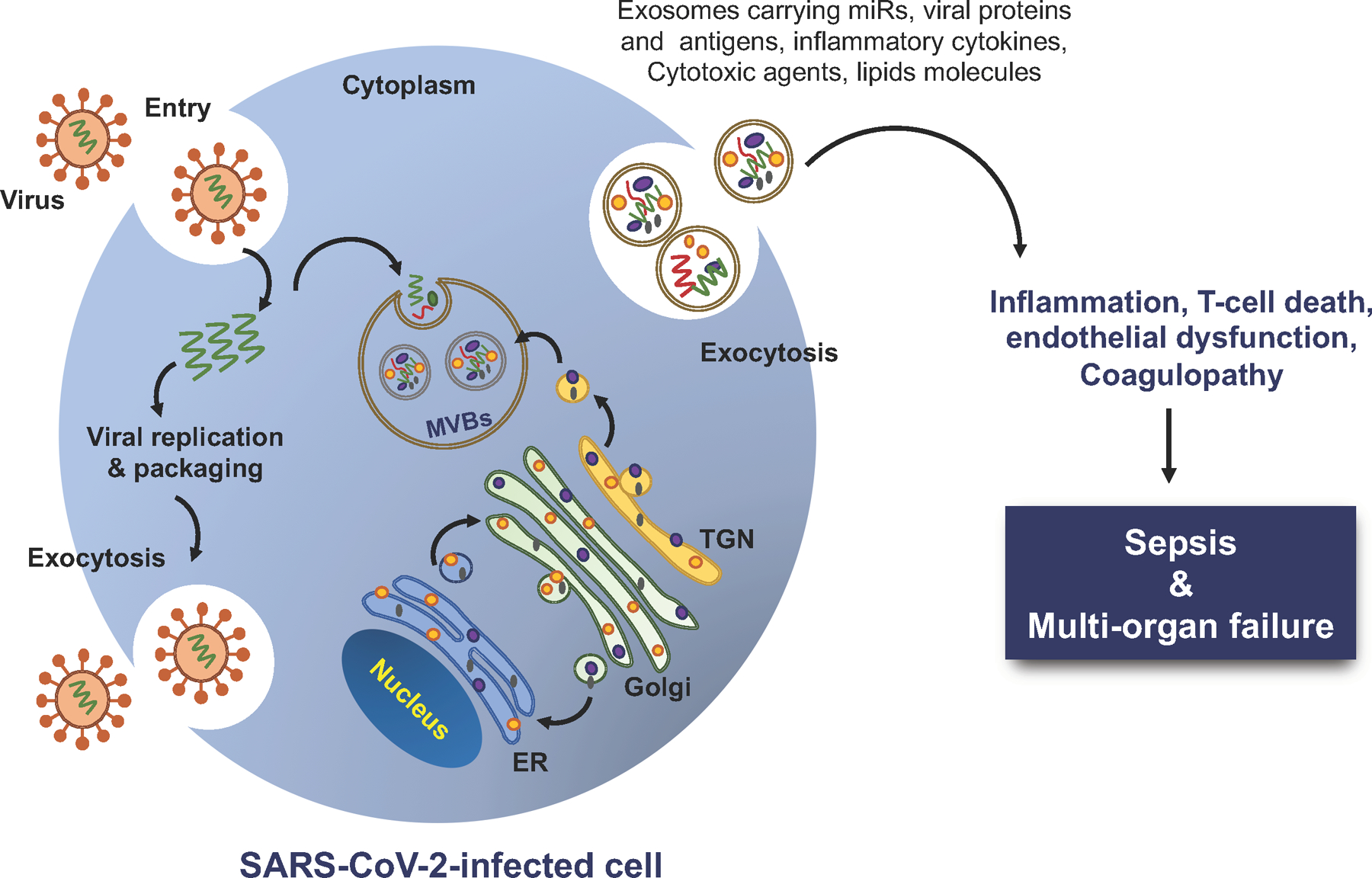
Exosomes derived from virus-infected cells promote sepsis and tissue injury. Exosomes from virus-infected cells are packaged with bioactive molecules, including miRs, viral proteins, inflammatory cytokines, cytotoxic agents, and lipids that incite inflammation, activate endothelium, and affect intravascular coagulation leading to sepsis-like condition.
