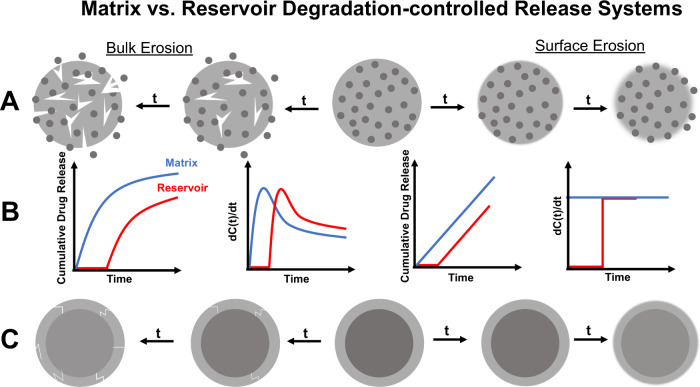
Fig. 4. Degradable polymeric systems can erode by different mechanisms depending on their chemical structure and mechanial properties. This factor, along with how the drug is incorporated into the matrix will ultimately impact how drug elution from the system occurs.
Controlled delivery systems can incorporate drug in a matrix (A, B) or a reservoir (B, C) system. Depending on the application, this will alter the drug release from the system in a specific manner. Reservoir systems are characteristic of a delayed release as the polymer surrounding the drug core degrades whereas matrix systems will depend more highly on the polymer-drug interactions among other factors (B). If solely based on polymer degradation, however, the release will either be more exponential (bulk erosion) or continual (surface erosion). Bulk erosion usually provides the system a “burst” release at early time points, followed by a continuous decrease in rate.