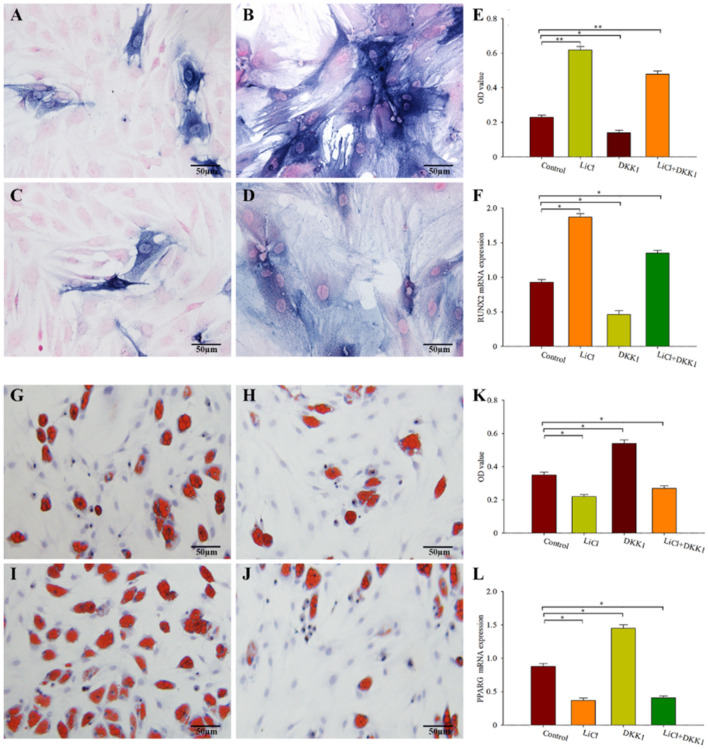
Figure 2.
Lithium induces osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by regulating Wnt signaling pathway. (A) Bone BMSCs were positively stained with ALP after 14 days of culture in osteogenic medium (magnification: 400 times). (B) The number of ALP positive staining of BMSCs increased significantly after 14 days of cultivation in osteogenic medium containing LiCl (12 mM) (magnification factor: 400 times). (C) DKK1 significantly inhibits the osteoblast differentiation (magnification: 400 times); (D) LiCl was added to the medium and ALP positive staining were increased again (magnification factor: 400). (E) The results of statistical analysis of the optical density of ALP positive staining in the four groups were: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with the control group. (F) Expression multiplication of marker gene RUNX2 in Wnt signaling pathway was detected by RT-PCR, *P < 0.01 compared with the control group. (A) BMSCs were positive for oil red O staining after 14 days of culture in adipogenic medium, forming characteristic red lipid droplets (magnification: 400 times). (B) The number of lipid droplets formed by BMSCs cocultured with LiCl decreased significantly (magnification: 400 times). (C) DKK1 significantly increases lipid droplet formation (magnification: 400 times). (D) LiCl was added to the medium and a small amount of lipid droplets could be observed (magnification: 400 times). (E) Statistical analysis results of optical density values of lipid droplets in each group, *P < 0.01 compared with the control group. (F) mRNA expression of PPARG was detected by RT-PCR, *P < 0.01 compared with the control group. Three fields of view were taken for each group, and the data were plotted in the format of mean ± standard deviation.