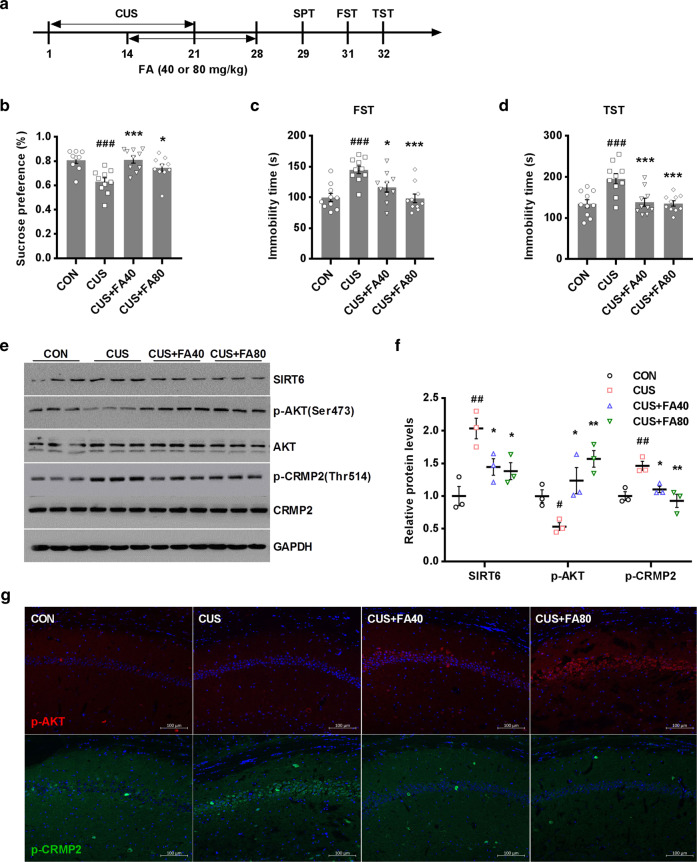
Fig. 6.
FA attenuates CUS-induced depression-like behaviors in mice as a pharmacological inhibitor of SIRT6. a Experimental procedure for the CUS-induced mouse model. Mice underwent a 21-day chronic stress. From day 15, mice were administered FA (40 or 80 mg· kg−1) for 14 days. b–d FA treatment completely prevented CUS-induced depression-like behaviors, including SPT (F3, 35 = 8.167, P = 0.0003), FST (F3, 36 = 9.859, P < 0.0001), and TST (F3, 36 = 9.907, P = 0.0001). The data are expressed as mean ± SEM. (n = 10 per group). ###P < 0.001 compared with CON group; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 compared with CUS group. e, f Western blotting analysis of SIRT6, phospho-AKT and phospho-CRMP2 protein level in the hippocampus. The data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3 per group). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 compared with CON group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with CUS group. g Immunostaining images showed that pharmacological inhibition of SIRT6 by FA treatment increased the expression of phospho-AKT and decreased the expression of phospho-CRMP2 in the hippocampus. Scale bar, 100 μm