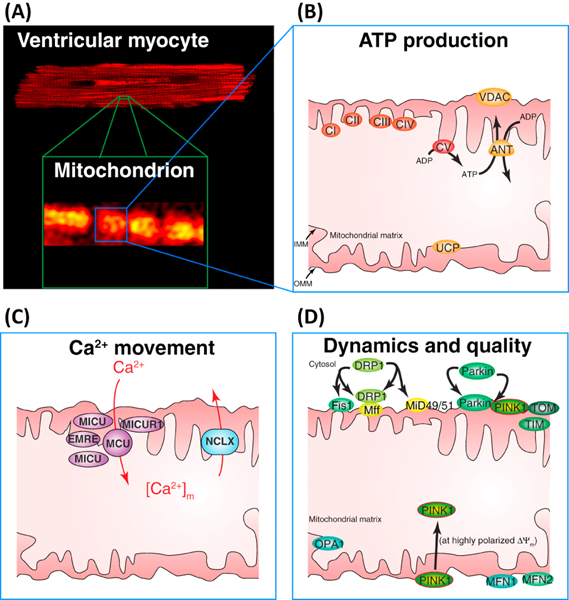
Figure 3. ATP production, Ca2+ movement, and mitochondrial dynamics in the inner (IMM) and outer mitochondrial membranes (OMM) in ventricular myocytes.
A. Top, confocal image of a ventricular cardiomyocyte showing the fluorescence of TMRM in mitochondria. Bottom, zoomed-in view showing a small region of the cell with 4–6 mitochondria. B. Schematic diagram of one of the intermyofibrillar mitochondria. The electron transport chain (ECT) is composed of five complexes: CI CII, CIII, CIV and CV. CI-CIV extrude protons to hyperpolarize IMM to approximately −160 mV. CV (the ATP synthase), uses the energy in ΔΨM to phosphorylate ADP to produce ATP. The adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) exchanges ADP for ATP across the IMM. The voltage dependent anion channel is permeant to ATP, ADP, Ca2+, etc. The uncoupling proteins (UCPs) on the IMM regulates proton movement from the intermembrane space to the matrix in the production of heat. C. Mitochondrial Ca2+ entry and exit. MCU responsible for Ca2+ entry across the IMM is composed of the MCU, EMRE and MICUR1 subunits and is probably associated with one or more MICU1 (or MICU2 or MICU3) proteins. Ca2+ is extruded from the matrix by the Na+ dependent Ca2+ transporter, NCLX (also called the mitochondrial NCX, Na+-Ca2+ exchanger). D. Proteins involved with mitochondrial dynamics and quality control: OMM: Drp1 which associates with Fis1, Miff, MiD49/51; Parkin and PINK1; translocase of the OMM (Tom) complex, Mfn1, Mfn2. IMM: Opa1, translocase of the IMM (Tim) complex. Note: Tom and Tim proteins form a mitochondrial protein import path.