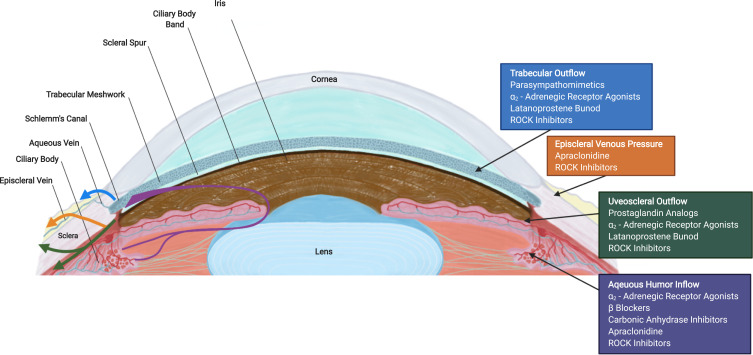
Figure 1.
Cross section of an eye illustrating aqueous humor (AH) pathways (left) and site of action of antiglaucoma medications (right). AH formation occurs in the ciliary body and flows from the posterior chamber through the pupil to the anterior chamber angle. The drainage of AH is mainly facilitated by the conventional [trabecular meshwork (TM), Schlemm’s canal and episcleral veins] pathway and the non-conventional (uveoscleral-uveovortex) pathway. The current glaucoma hypotensive medications and their sites of action are shown on the right.
Abbreviation: ROCK, rho kinase.