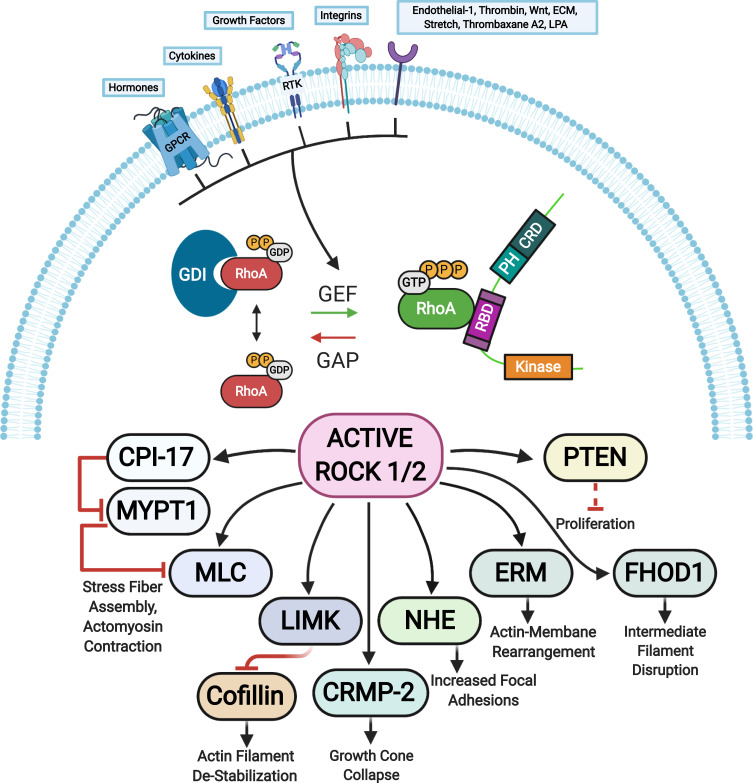
Figure 3.
ROCK targets. Rho proteins can be activated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs). GEFs are themselves activated and regulated via engagement of various receptors at the plasma membrane. The active GTP-bound Rho subsequently activates ROCK 1 and ROCK 2 that phosphorylate various substrates resulting in diverse cellular responses. The barred-line notation indicates inhibition and the arrows show the cascade of the molecular response. Adapted from Hartmann S, Ridley AJ, Lutz S. The function of rho-associated kinasesROCK1 and ROCK2 in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease.Front Pharmacol. 2015;6(276):1–16. Copyright © 2015 Hartmann, Ridley and Lutz. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.14
Abbreviations: CPI-17, kinase C-potentiated phosphatase inhibitor of 17 kDa; CRMP-2, collapsin response mediator protein 2; ECM, extracellular matrix; ERM, ezrin-radixin-moesin; FHOD1, formin homology 2 domain-containing 1; GAP, GTPase activating protein; GPCRs, G protein-coupled receptors; LIMK, LIM-kinase; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; MLC, myosin II regulatory light chain; MYPT1, myosin phosphatase target subunit 1; NHE, Na+/H+ exchanger; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinases; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; GDI, guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor; P, phosphate; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; RhoA, Ras homolog family member A.