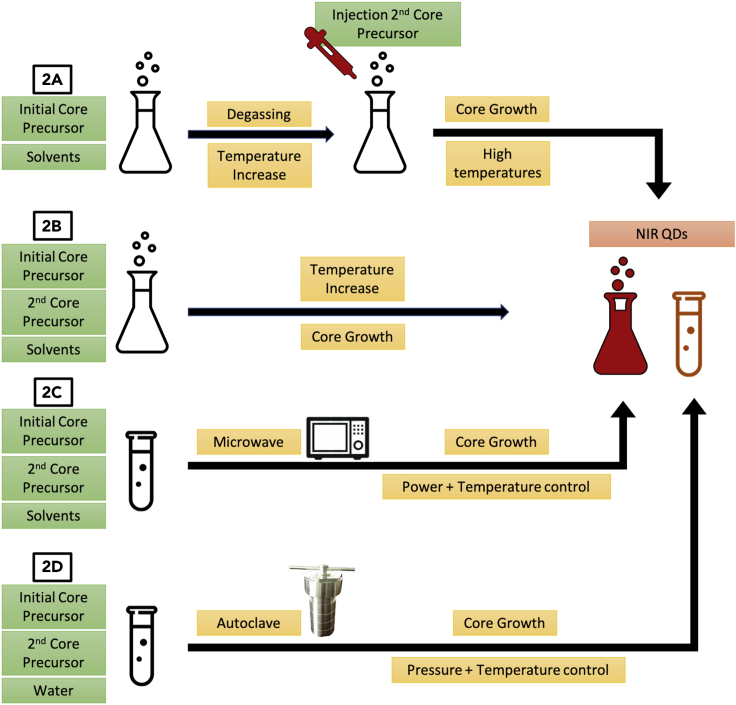
Figure 2.
Overview of the synthetic methodologies used for NIR QDs
(A–D) (2A) Hot-injection: in the first step, one initial precursor is mixed with the reaction solvent and degassed under vacuum and argon. Then, the temperature is elevated close to the nucleation temperature and the second core precursor is injected. The core growth is performed at high temperature and the NIR QDs are synthesized; (2B) Heat-up: all of the core precursors and reaction solvents are mixed at room temperature, and the temperature is gradually increased up to the nucleation threshold. Core growth takes place and NIR QDs are synthesized; (2C) Microwave: similar to the heat-up method, QD precursors and reaction solvents are mixed in a microwave vessel. The vessel is then placed in a microwave and submitted to controlled power and temperature output for a short period of time. (2D) Hydrothermal: precursors are mixed in water at room temperature and then added to a Teflon-lined autoclave. The system is closed and submitted to high temperature and pressure, allowing the formation of water-soluble NIR QDs.