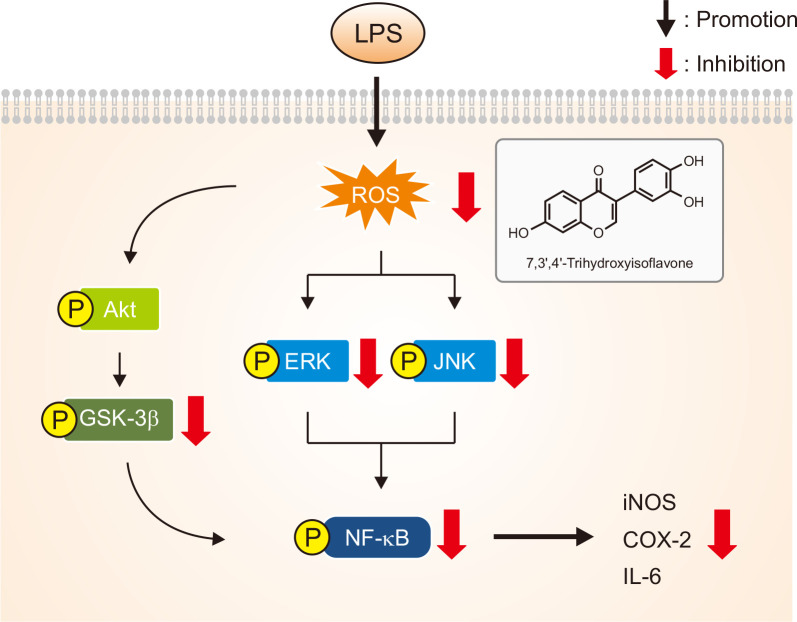
Fig. 6.
Proposed schematic of the molecular mechanisms of the effects of 7,3’,4’-THIF on LPS-induced neuroinflammation in BV2 microglial cells. LPS induces phosphorylation of MAPK signaling molecules (JNK and ERK 1/2) as well as GSK-3β and NF-κB. This activation of NF-κB induces expression of its target genes such as iNOS and COX-2, resulting in the production of NO and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, and in the accumulation of ROS. Release of these inflammatory mediators leads to neuroinflammation and neuronal cell injury. Pretreatment of BV2 microglial cells with 7,3’,4’-THIF inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses through inhibition of MAPK signaling molecules and GSK-3β and NF-κB.