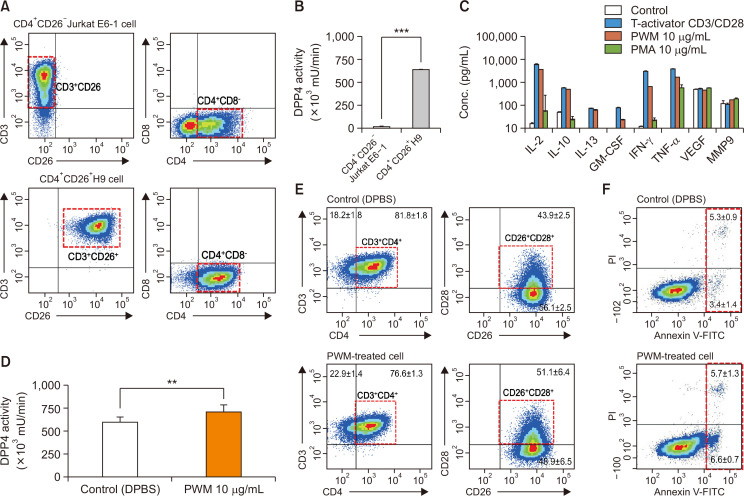
Fig. 1.
Characterization of CD26 expression, mDPP4 enzymatic activity, and cytokine expression in T helper cell lines. (A, B) Jurkat E6 and H9 Th1 cells were harvested and analyzed for the expression of T cell-specific surface markers, including CD3, CD4, and CD26 (A), and for their mDPP4 enzymatic activity (B). (C) H9 Th1 cells were treated with various T cell activators, including T-Activator CD3/CD28, PWM (10 µg/mL), and PMA (10 µg/mL) for 3 h. The expressions of 18 cytokines and 6 MMPs were measured in the culture supernatants of treated cells using two different panels of fluorescent multiplex bead assays. Activated T helper cell-specific cytokines, including IL-2, IL-10, IL-13, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, and TNF-α, are shown. VEGF and MMP 9 are also included as detected high in all the samples. (D-F) H9 Th1 cells were treated with 10 µg/mL PWM for 12 h and subjected to mDPP4 enzymatic assays (D), FACS analysis for T helper cell-specific surface markers such as CD3, CD4, CD26, and CD28 (E), and analysis for apoptosis using an annexin V kit and flow cytometry (F). All analyses were repeated in three independent batches, and the data are shown as the means and standard deviation. **p<0.005; ***p<0.001 (paired t-test).