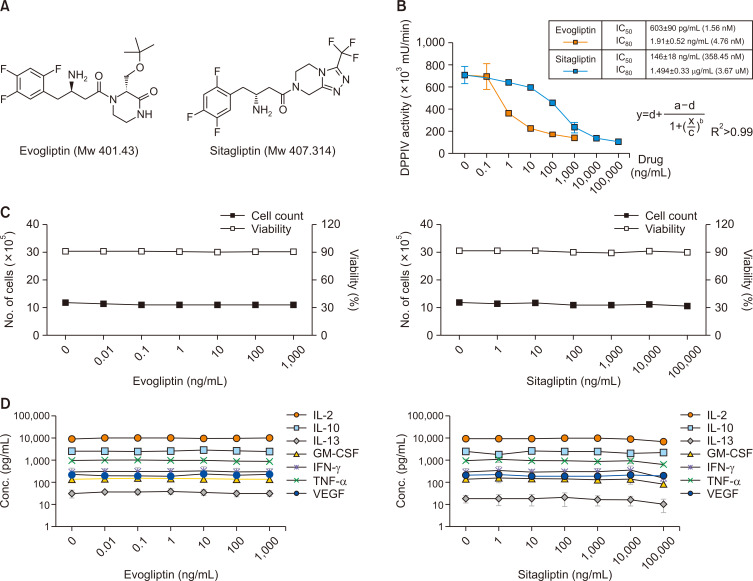
Fig. 2.
Effects of antidiabetic drugs on mDPP4 enzymatic activity, cell profiles, and Th1-specific cytokine expression in H9 Th1 cells. (A) The chemical structures of antidiabetic drugs, evogliptin and sitagliptin, are shown. (B-D) Cell pellets and culture supernatants were harvested 12 h after treatment of H9 Th1 cells with evogliptin (dose range, 0-1 µg/mL) or sitagliptin (dose range, 0-100 µg/mL) in the presence of 10 µg/mL PWM. The mDPP4 enzymatic activity of the cell pellets was measured using a spectrofluorometer, and the IC50 values of these drugs were determined using a series of dose-response curve fits for mDPP4 enzymatic activity (B). The cell profiles, including cell number and viability, of the PWM-treated cells with or without antidiabetic drugs were assessed using an automatic cell counter (C). The values of Th1-specific cytokines, including IL-2, IL-10, IL-13, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and GM-CSF, and VEGF in the culture supernatants were quantified using a fluorescent multiplex bead assay (D). These analyses were performed in over three independent batches, and the data are shown as means and standard deviation.